3
{
When a station shuts down a VM, it sends a VDP de-associate packet to the bridge. The
bridge sends the request to the VSI manager, and the VSI manager notifies the bridge to
delete the VSI interface.
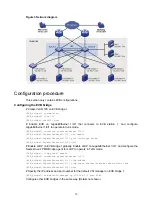
An EVB station and an EVB bridge perform the following steps to manage VM traffic:
1.
Use CDCP to establish an S-channel.
2.
Exchange EVB TLVs through LLDP to negotiate EVB capabilities such as RR, ECP parameters,
and VDP parameters for the S-channel.
3.
Use VDP to associate the VSIs of VMs with the bridge port.
Protocols and standards
IEEE P802.1Qbg/D2.2, Draft Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks—MAC Bridges
and Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks - Amendment XX: Edge Virtual Bridging
Feature and hardware compatibility
EVB is applicable only to interfaces on the following modules:
•
EC interface modules.
•
SE interface modules:
{
LSU1CGC2SE0.
{
LSUM2GP24TSSE0.
{
LSUM2GP44TSSE0.
{
LSUM2GT24PTSSE0.
{
LSUM2GT24TSSE0.
{
LSUM2GT48SE0.
{
LSUM2GV48SE0.
•
SF interface modules.
•
SG interface modules.
Traffic received from an EVB-enabled interface can be forwarded only through interface modules
that support EVB.
Licensing requirements
EVB requires a license to run on the device. For information about obtaining a license, see
Fundamentals Configuration Guide
.
Configuration restrictions and guidelines
EVB and feature compatibility
shows features incompatible with EVB and the references for these features.
Table 1 Features incompatible with EVB
Feature Reference
EVI
EVI Configuration Guide