GP-L200N User Manual
31
Access Category
Description
802.1d
Tags
long delays, such as Internet surfing
WMM Background
Priority
Low priority traffic (file downloads, print jobs)
that does not have strict latency and throughput
requirements
2, 1
AC_VO: Voice (highest priority)
AC_VI: Video (high priority)
AC_BE: Best effort (medium priority)
AC_BK: Background (low priority)
802.11 uses DCF (Distributed Coordination Function) scheme of the CSMA/CA
(Carrier Sense Multiple Access / Collision Avoidance) protocol to reduce the
chances of packets collision while one more devices access the wireless media at
the same time. A client wishing to transmit has to first listen to the channel for a
predetermined amount of time so as to check for any activity on the channel. If the
channel is sensed "idle" then the client is permitted to transmit. If the channel is
sensed as "busy" the station has to defer its transmission. The random interval
provides a fair transmission chance for all the devices.
When each priority queue waits for sending packets, it has to wait a fixed time
AIFSN and a random time CW. They define time values by multiple time slots. For
802.11b, its time slot is 20ms. The time slot of 802.11a and 802.11g is 9 ms. CW
insures the random delay time of DCF, so that the packets collision among the
devices with the same access category can be avoided. If collision occurs, CW is
doubled until exceeds its maximum value. After every successful transmission, CW
returns to the minimum value.
The priority queue that succeeds in the competition of sending packets, it will
acquire Txop time to send packets. If the txop value is 0, it is limited to be a MSDC
(MAC Service Data Unit).
(2)
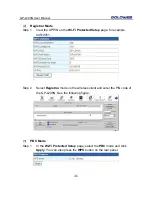
Set WMM Parameters
In the
Wi-Fi Multimedia
pane, click
WMM Configuration
and the following page
appears: