4
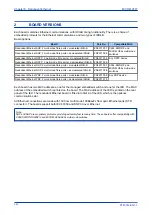
REDUNDANCY PROTOCOLS
The following redundancy protocols are available:
●
PRP (Parallel Redundancy Protocol)
●
RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol)
●
SHP (Self-Healing Protocol)
●
DHP (Dual Homing Protocol)
The protocol must be selected at the time of ordering.
4.1
PARALLEL REDUNDANCY PROTOCOL (PRP)
Power system companies have traditionally used proprietary protocols for redundant communications. This is
because standardized protocols could not meet the requirements for real-time systems. Even a short loss of
connectivity may result in loss of functionality.
However, Parallel Redundancy Protocol (PRP) uses the IEC 62439 standard in Dual Homing Star Topology
networks, designed for IEDs from different manufacturers to operate with each other in a substation
redundant-Ethernet network. PRP provides bumpless redundancy for real-time systems and is the standard
for double Star-topology networks in substations.
4.1.1
PRP NETWORKS
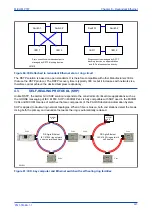
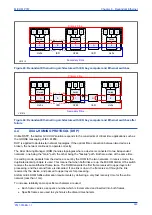
Redundant networks usually rely on the network’s ability to reconfigure if there is a failure. However, PRP
uses two independent networks in parallel.
PRP implements the redundancy functions in the end nodes rather than in network elements. This is one
major difference to RSTP. An end node is attached to two similar LANs of any topology which operate in
parallel.
The sending node replicates each frame and transmits them over both networks. The receiving node
processes the frame that arrives first and discards the duplicate. Therefore there is no distinction between
the working and backup path. The receiving node checks that all frames arrive in sequence and that frames
are correctly received on both ports.
The PRP layer manages this replicate and discard function, and hides the two networks from the upper
layers. This scheme works without reconfiguration and switchover, so it stays available ensuring no data
loss.
There should be no common point of failure between the two LANs. Therefore they are not powered by the
same source and cannot be connected directly together. They are identical in protocol at the MAC level but
may differ in performance and topology. Both LANs must be on the same subnet so all IP addresses must be
unique.
4.1.2
NETWORK ELEMENTS
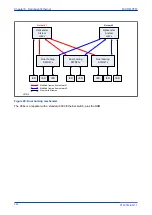
A PRP compatible device has two ports that operate in parallel. Each port is connected to a separate LAN. In
the IEC 62439 standard, these devices are called DANP (Doubly Attached Node running PRP). A DAN has
two ports, one MAC address and one IP address.
A Single Attached Node (SAN) is a non-critical node attached to only one LAN. SANs that need to
communicate with each other must be on the same LAN.
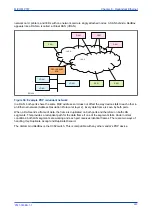
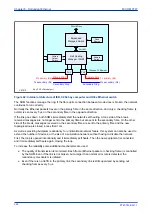
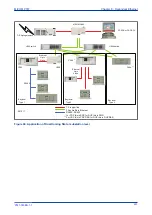
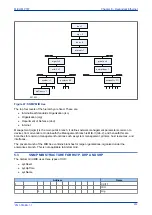
The following diagram shows an example of a PRP network. The Doubly Attached Nodes DANP 1 and
DANP 2 have full node redundancy. The Singly Attached Nodes SAN 1 and SAN 4 do not have any
redundancy. Singly attached nodes can be connected to both LANs using a Redundancy Box (RedBox). The
RedBox converts a singly attached node into a doubly attached node. Devices such as PCs with one
Chapter 8 - Redundant Ethernet
MiCOM P747
244
P747-TM-EN-1
P747-TM-EN-1.1
Summary of Contents for MiCOM P747 Agile
Page 2: ......
Page 16: ...Contents MiCOM P747 xiv P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 20: ...Table of Figures MiCOM P747 xviii P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 21: ...INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 1...
Page 22: ...Chapter 1 Introduction MiCOM P747 2 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 31: ...SAFETY INFORMATION CHAPTER 2...
Page 32: ...Chapter 2 Safety Information MiCOM P747 12 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 42: ...Chapter 2 Safety Information MiCOM P747 22 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 43: ...HARDWARE DESIGN CHAPTER 3...
Page 44: ...Chapter 3 Hardware Design MiCOM P747 24 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 74: ...Chapter 3 Hardware Design MiCOM P747 54 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 75: ...CONFIGURATION CHAPTER 4...
Page 76: ...Chapter 4 Configuration MiCOM P747 56 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 117: ...PROTECTION FUNCTIONS CHAPTER 5...
Page 118: ...Chapter 5 Protection Functions MiCOM P747 98 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 160: ...Chapter 5 Protection Functions MiCOM P747 140 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 161: ...MONITORING AND CONTROL CHAPTER 6...
Page 162: ...Chapter 6 Monitoring and Control MiCOM P747 142 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 211: ...SCADA COMMUNICATIONS CHAPTER 7...
Page 212: ...Chapter 7 SCADA Communications MiCOM P747 192 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 259: ...REDUNDANT ETHERNET CHAPTER 8...
Page 260: ...Chapter 8 Redundant Ethernet MiCOM P747 240 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 293: ...CYBER SECURITY CHAPTER 9...
Page 294: ...Chapter 9 Cyber Security MiCOM P747 274 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 313: ...SETTINGS APPLICATION SOFTWARE CHAPTER 10...
Page 314: ...Chapter 10 Settings Application Software MiCOM P747 294 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 322: ...Chapter 10 Settings Application Software MiCOM P747 302 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 323: ...BUSBAR COMMISSIONING TOOL CHAPTER 11...
Page 324: ...Chapter 11 Busbar Commissioning Tool MiCOM P747 304 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 330: ...Chapter 11 Busbar Commissioning Tool MiCOM P747 310 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 331: ...SCHEME LOGIC CHAPTER 12...
Page 332: ...Chapter 12 Scheme Logic MiCOM P747 312 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 348: ...Chapter 12 Scheme Logic MiCOM P747 328 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 349: ...INSTALLATION CHAPTER 13...
Page 350: ...Chapter 13 Installation MiCOM P747 330 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 361: ...COMMISSIONING INSTRUCTIONS CHAPTER 14...
Page 362: ...Chapter 14 Commissioning Instructions MiCOM P747 342 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 387: ...MAINTENANCE AND TROUBLESHOOTING CHAPTER 15...
Page 388: ...Chapter 15 Maintenance and Troubleshooting MiCOM P747 368 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 403: ...TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS CHAPTER 16...
Page 404: ...Chapter 16 Technical Specifications MiCOM P747 384 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 425: ...SYMBOLS AND GLOSSARY APPENDIX A...
Page 426: ...Appendix A Symbols and Glossary MiCOM P747 406 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 443: ...COMMISSIONING RECORD APPENDIX B...
Page 444: ...Appendix B Commissioning Record MiCOM P747 424 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 449: ...WIRING DIAGRAMS APPENDIX C...
Page 450: ...Appendix C Wiring Diagrams MiCOM P747 430 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 456: ...Appendix C Wiring Diagrams MiCOM P747 436 P747 TM EN 1 P747 TM EN 1 1...
Page 457: ......