CHAPTER 1: COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
MODBUS FUNCTIONS
345 TRANSFORMER PROTECTION SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
1–171
MODBUS Functions
Function Code 03H
Modbus implementation: Read Holding Registers
345 implementation: Read Setpoints
For the 345 implementation of Modbus, this function code can be used to read any
setpoints (“holding registers”). Holding registers are 16 bit (two byte) values transmitted
high order byte first. Thus all 345 Setpoints are sent as two bytes. The maximum number of
registers that can be read in one transmission is 125.
The slave response to this function code is the slave address, function code, a count of the
number of data bytes to follow, the data itself and the CRC. Each data item is sent as a two
byte number with the high order byte sent first.
For example, consider a request for slave 17 to respond with 3 registers starting at address
006B. For this example the register data in these addresses is as follows:
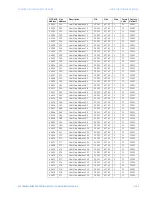
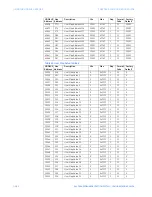
The master/slave packets have the following format:
Table 33: MASTER/SLAVE PACKET FORMAT FOR FUNCTION CODE 03H
Function Code 04H
Modbus Implementation: Read Input Registers
345 implementation: Read Actual Values
Address
Data
006B
022B
006C
0000
006D
0064
MASTER TRANSMISSION
BYTES
EXAMPLE
DESCRIPTION
SLAVE ADDRESS
1
11
message for slave 17
FUNCTION CODE
1
03
read registers
DATA STARTING ADDRESS
2
00 6B
data starting at
006B
NUMBER OF SETPOINTS
2
00 03
3 registers = 6 bytes
total
CRC
2
76 87
CRC error code
SLAVE RESPONSE
BYTES
EXAMPLE
DESCRIPTION
SLAVE ADDRESS
1
11
message from slave
17
FUNCTION CODE
1
03
read registers
BYTE COUNT
1
06
3 registers = 6 bytes
DATA 1 (see definition above)
2
02 2B
value in address
006B
DATA 2 (see definition above)
2
00 00
value in address
006C
DATA 3 (see definition above)
2
00 64
value in address
006D
CRC
2
54 83
CRC error code