- 17 -
16. BATTERY’S CAPACITY CALCULATION
The battery’s back up time depends on the battery capacity(Ah) and your appliances power (Watt). The method to calculate the
operation time is:
Battery capacity(Ah) x input voltage/ loads power(W)
For example:
Battery capacity = 150Ah
Input Voltage = 12V
Loads power = 600W
(150Ah x 12V)/600W = 3H
17. TROUBLESHOOTING
This section describes the most common problems you may encounter with the operation of the inverter along with solutions.
If you encounter problems other than what is described in this section, contact customer supporting center.
17.1 COMMON PROBLEMS
Buzz in audio equipment
Some inexpensive stereo systems may emit a buzzing noise from their loudspeakers when operated the inverter. This occurs
because the power supply in the audio System does not adequately filter the modified sine wave produced by the inverter.
The only solution is to use a sound system that has a high quallty power supply.
Television reception
When the inverter is operating, it can interfere with televisionReception on some channels. If interference occurs, try the
following:
1. Make sure that the chassis ground screw on the rear of the inverter is solidly connected to the ground system of your
vehicle or home.
2. Make sure that the television antenna provides an adequate (“snow-free”) signal and that you are using good quality
cable between the antenna and the television.
3. Keep the cables between the battery and the inverter as short as possible, and twist them together with two to three
twists per foot (this minimizes radiated interference from the cables).
4. Move the television as far away from the inverter as possible.
5. Do not operate high power loads with the inverter when the television is on.
Danger
ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARD
• Do not disassemble the Inverter. It does not contain any user-serviceable parts.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death or serious injury.
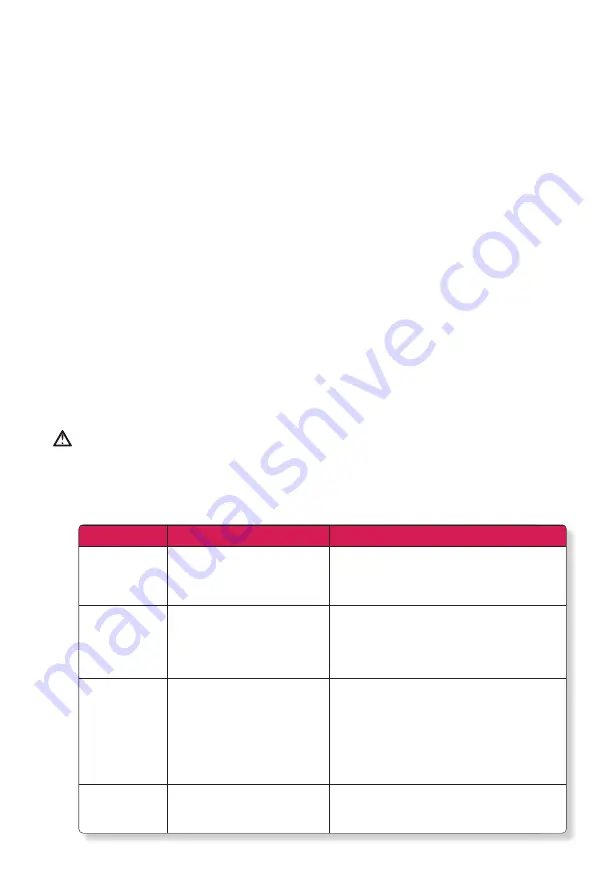
17.2 TABLE 1 - TROUBLESHOOTING REFERENCE
Problem
Possible cause
Solution
Low output voltage
You are using a voltmeter that
cannot accurately read the RMS
voltage of a modified sine wave.
Low input voltage and the load is
close to maximum allowable power.
Use a true RMS reading voltmeter such as the Fluke87.
Check the connections and cable to see if the battery
is fully charged. Recharge the battery if it is low.
Reduce the load.
No output voltage.
Both the power
light and fault light
are off
The inverter is off.
No power to the inverter.
The inverter could have been
connected with reverse DC input
polarity.
Turn the inverter on.
Check the wiring to the inverter and he battery selector
switch
(if installed). The inverter has probably been damaged.
Return the unit, damage caused by reverse polarity is
not covered by the warranty.
No output voltage.
Fault light is on
Low input voltage.
High input voltage.
Thermal shutdown.
Unit overload.
Output is short circuited.
Recharge the battery, check the connections and
cable. Make sure the inverter is connected to a correct
battery (12V inverter for 12V battery or batteries bank).
Allow the unit to cool off. Reduce the load if continuous
operation is required. lmprove ventilation. Make sure
the inverter’s ventilation openings are not obstructed.
Reduce the ambient temperature. Reduce the load.
Make sure the load does not exceed the inverter’s
output rating. Remove the short circuit
Low battery alarm
stays on
Poor DC wiring, poor battery
condition
Use proper cable size and lengths and make solid
connections.
Charge the battery.
Install a new battery.



































