MB95630H Series
78
FUJITSU SEMICONDUCTOR LIMITED
MN702-00009-1v0-E
CHAPTER 5 INTERRUPTS
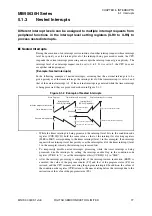
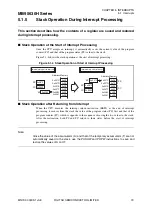
5.1 Interrupts
5.1.4
Interrupt Processing Time
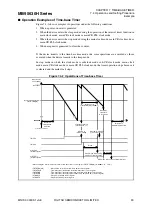
Before the CPU enters the interrupt service routine after an interrupt request is
made, it needs to wait for the interrupt processing time, which consists of the
time between the occurrence of an interrupt request and the end of the
execution of the instruction being executed, and the interrupt handling time
(the time required to initiate interrupt processing) to elapse. The maximum
interrupt processing time is 26 machine clock cycles.
■
Interrupt Processing Time
Before executing the interrupt service routine after an interrupt request is made, the CPU needs
to wait for the interrupt request sampling wait time and the interrupt handling time to elapse.
●
Interrupt request sampling wait time
The CPU decides whether an interrupt request has occurred by sampling the interrupt request
during the last cycle of an instruction. Therefore, the CPU cannot recognize interrupt requests
while executing an instruction. This sampling wait time reaches its maximum when an
interrupt request occurs immediately after the CPU starts executing the DIVU instruction,
whose execution cycle is the longest (17 machine clock cycles).
●
Interrupt handling time
After accepting an interrupt, the CPU requires nine machine clock cycles to perform the
following interrupt processing setup:
•
Saves the value of the program counter (PC) and that of the program status (PS) to the
stack.
•
Sets the PC to the start address (interrupt vector) of interrupt service routine.
•
Updates the interrupt level bits (CCR:IL[1:0]) in the program status (PS).
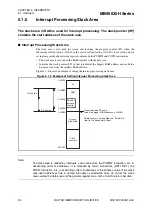
Figure 5.1-3 Interrupt Processing Time
When an interrupt request occurs immediately after the CPU starts executing the DIVU
instruction, whose execution cycle is the longest (17 machine clock cycles), the interrupt
processing time spans 26 machine clock cycles.
The span of a machine clock cycle varies depending on the clock mode and main clock speed
change (gear function). For details, see "CHAPTER 3 CLOCK CONTROLLER".
CPU oper
a
tion
Interr
u
pt w
a
it time
Interr
u
pt re
qu
e
s
t
sa
mpling w
a
it time
Norm
a
l in
s
tr
u
ction exec
u
tion
Interr
u
pt h
a
ndling time
(9 m
a
chine clock cycle
s
)
Interr
u
pt h
a
ndling
Interr
u
pt
s
ervice ro
u
tine
Interr
u
pt re
qu
e
s
t gener
a
ted
: L
as
t in
s
tr
u
ction cycle in which the interr
u
pt re
qu
e
s
t i
s
sa
mpled