MB95630H Series
MN702-00009-1v0-E
FUJITSU SEMICONDUCTOR LIMITED
77
CHAPTER 5 INTERRUPTS
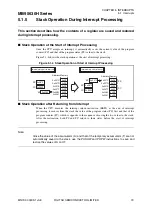
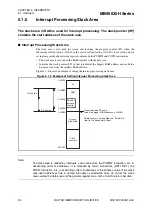
5.1 Interrupts
5.1.3
Nested Interrupts
Different interrupt levels can be assigned to multiple interrupt requests from
peripheral functions in the interrupt level setting registers (ILR0 to ILR5) to
process nested interrupts.
■
Nested Interrupts
During the execution of an interrupt service routine, if another interrupt request whose interrupt
level has priority over the interrupt level of the interrupt being processed is made, the CPU
suspends the current interrupt processing and accepts the interrupt request given priority. The
interrupt level of an interrupt request can be set to 0 to 3. If it is set to 3, the CPU does not
accept that interrupt request.
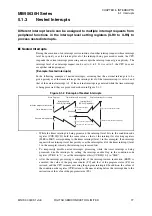
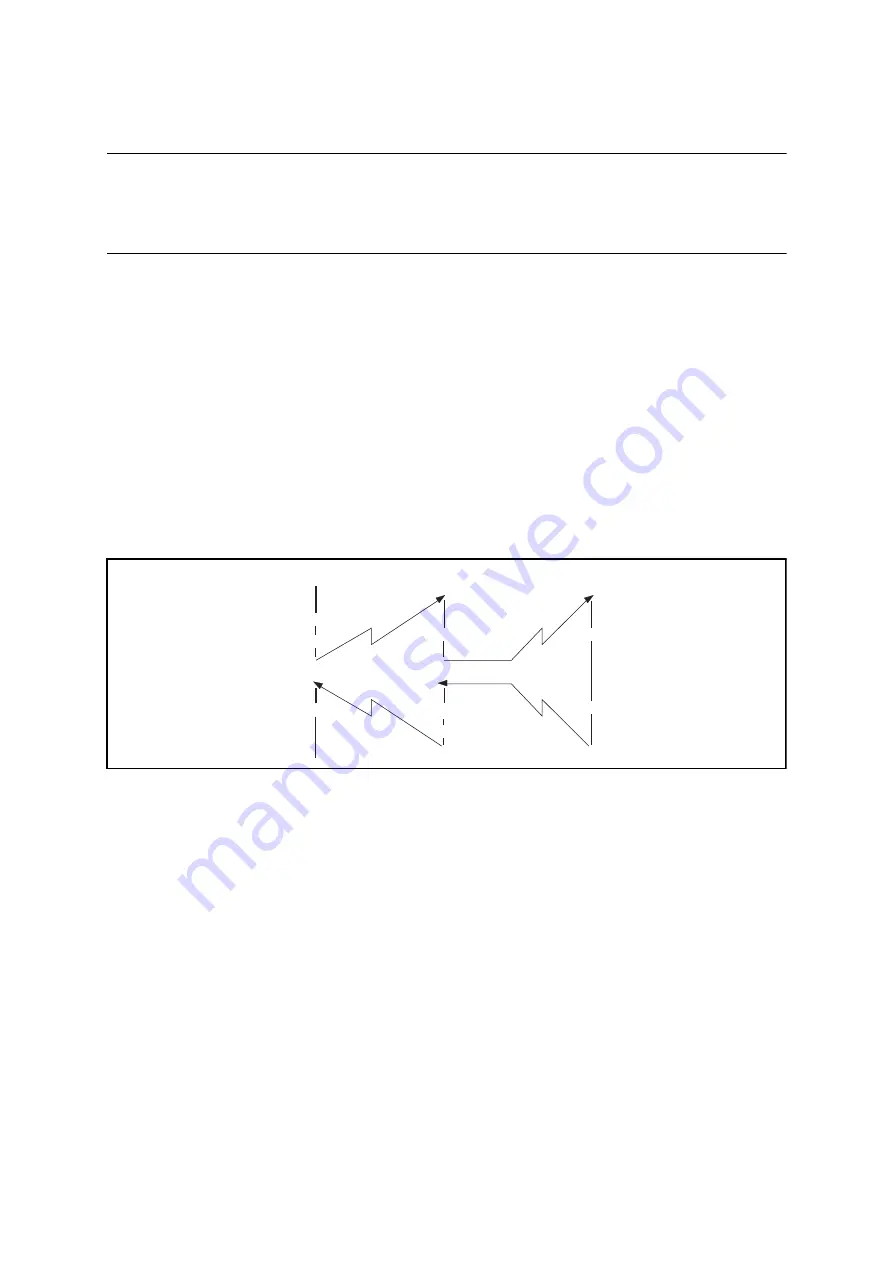
[Example: Nested interrupts]
In the following example of nested interrupts, assuming that the external interrupt is to be
given priority over the timer interrupt, the interrupt level of the timer interrupt is set to 2 and
that of the external interrupt to 1. If the external interrupt is generated while the timer interrupt
is being processed, they are processed as shown in Figure 5.1-2.
Figure 5.1-2 Example of Nested Interrupts
•
While the timer interrupt is being processed, the interrupt level bits in the condition code
register (CCR:IL[1:0]) hold the same value as that of the interrupt level setting registers
(ILR0 to ILR5) corresponding to the timer interrupt (level 2 in this example). If an interrupt
request whose interrupt level has priority over the interrupt level of the timer interrupt (level
1 in the example) is made, that interrupt is processed first.
•
To temporarily disable nested interrupts processing while the timer interrupt is being
processed, disable interrupts by setting the interrupt enable flag in the condition code
register (CCR:I) to "0", or set the interrupt level bits (CCR:IL[1:0]) to "0b00".
•
After the interrupt processing is completed, if the interrupt return instruction (RETI) is
executed, the value of the program counter (PC) and that of the program status (PS) are
restored, and the CPU resumes executing the program interrupted. In addition, the values of
the condition code register (CCR) return to the ones existing before the interrupt due to the
restoration of the value of the program status (PS).
(6)
Proce
ss
timer interr
u
pt
(7)
Ret
u
rn from timer interr
u
pt
(
3
)
Extern
a
l interr
u
pt
occ
u
r
s
(4)
Proce
ss
extern
a
l interr
u
pt
(5)
Ret
u
rn from extern
a
l interr
u
pt
Timer Interr
u
pt Proce
ss
ing
M
a
in Progr
a
m
Extern
a
l Interr
u
pt Proce
ss
ing
Interr
u
pt level 2
(CCR:IL[1:0]=0
b
10)
Initi
a
lize peripher
a
l re
s
o
u
rce
s
(1)
Timer interr
u
pt occ
u
r
s
(2)
Re
su
me m
a
in progr
a
m
(
8
)
Re
su
me
Interr
u
pt level 1
(CCR:IL[1:0]=0
b
01)
Sus
pend