F M C M 1 2 - H D O P E R A T I O N A N D M A I N T E N A N C E M A N U A L
13
•
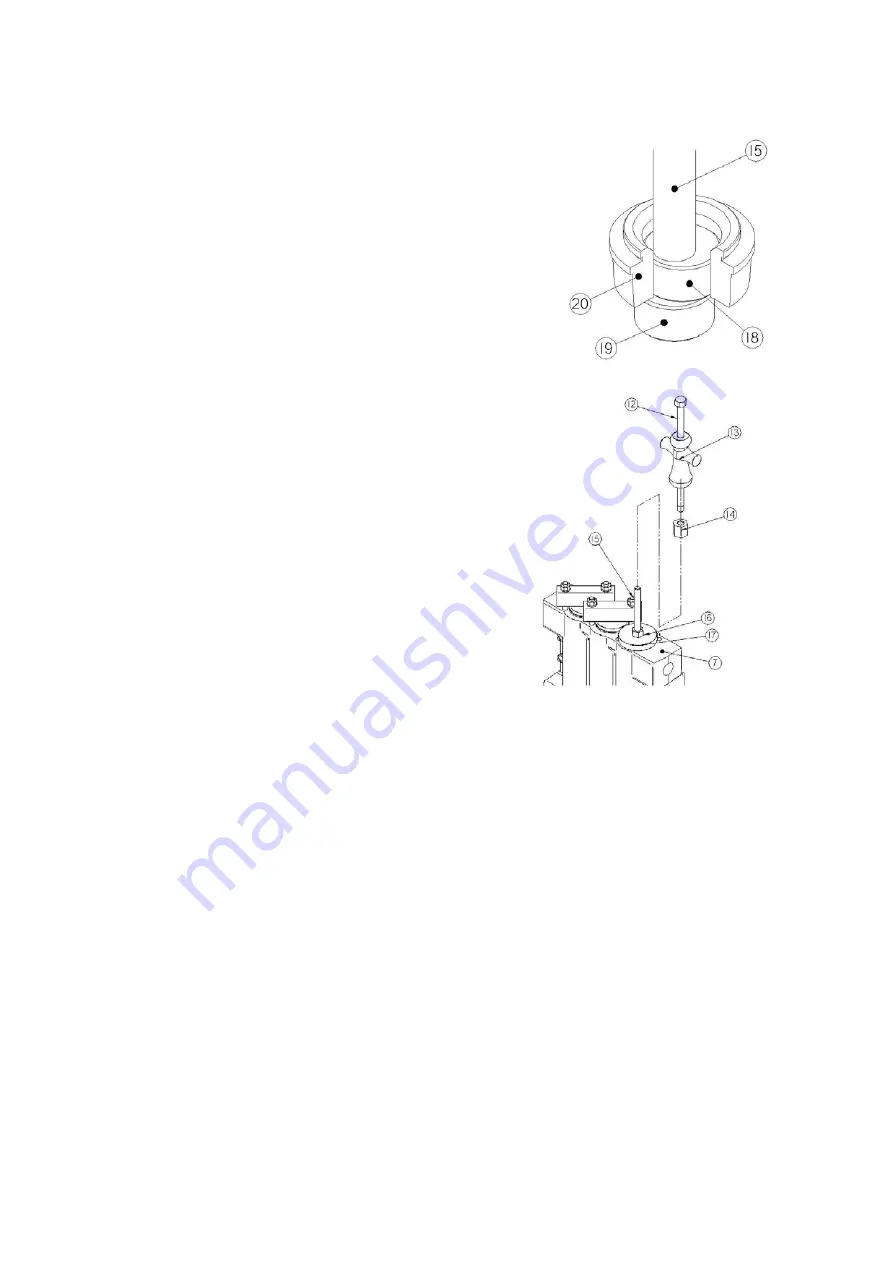
Assemble the puller guide (19) and puller eccentric (18)
on one end of the puller stem (15) as shown. There are
two guides and two eccentrics provided in the kit. Use the
slightly larger diameter ones to remove the discharge
valve seats. The smaller diameter components will be
used later when removing the suction valve seats.
•
Insert the end of the puller stem down through the discharge
valve seat (20). Work the puller guide (19) through the center
of the seat until it sits just underneath the seat. Hold the
puller stem firmly in position, then work from side to side until
the puller eccentric (18) drops down into the ID of the seat
and rests on the top of the guide as shown.
•
Hold the puller stem (15) in this position and slide
the strongback (17) down over the stem until it rests
squarely on the top of the fluid cylinder (7).
•
Run the puller nut (16) down the stem until it is hand
tight on the top of the strongback. You can now
release the puller stem, as the components will not
shift position with the nut in place.
•
Using a heavy-duty 1-5/8” wrench, tighten the puller
nut down against the strongback to apply force to
the bottom of the valve seat. Note that up to 800 ft-
lbs of torque may be required to free the valve seat
from the fluid cylinder. Do not exceed this value.
•
In many cases, torque alone will be sufficient to free
the valve seat. If unsuccessful with torque alone,
use the adapter nut (14) to connect the slide
hammer (13) and puller bolt (12) to the puller stem
(15). Leave the puller nut torqued from the previous
step. Drive the slide hammer firmly into the head of
the puller bolt to apply extra impact force to free the valve seat and lift out through the
valve cover bore in the fluid cylinder.
•
Repeat the previous steps to remove the suction valves that are located just below the
discharge valves. Replace the puller guide and eccentric with the smaller diameter parts
provided in the kit to slide through the smaller bore of the suction valve. It will be
necessary to fish out the valve spring and valve from the suction valve using a variety of
hooks and loops of string or wire since the are located too deeply in the bore of the fluid
cylinder to be removed by hand.
•
Remove the suction and discharge valves from the remaining two cylinders.
Summary of Contents for M12-HD
Page 1: ...M12 HD Piston Pump Operation Maintenance Manual ...
Page 19: ......




















