2. Fasten motor mounting kit, observe instruction manual
3. Fasten the motor without tension. Support large and heavy motors.
Connect motor cables only on completion of mounting.
6.4
Mounting the cylinder
High mechanical loads on the mounting connections
If high parallel torques are applied to the drive system at the same time, this leads
to high mechanical loads at the mounting interfaces.
• The foot mounting HNC, CRHNC should only be used in combination with the
profile mounting EAHF.
• In the case of an inclined or horizontal mounting position with direct fastening
or flange mounting EAHH-V2, the drive system must also be supported near
the motor mounting.
Requirement
–
No collision with mounting and sensor components in the movement space of
the attachment component.
–
Sufficient space to reach maintenance interfaces.
–
Sufficient space for reaching and mounting the pressure compensation port.
–
Flat mounting surface maximum 0.2 mm over the stroke length of the bearing
surface.
–
No distortion or bending when installing the product.
1. Select mounting attachments
2. Place the mounting attachments on the support points.
3. Tighten retaining screws.
Observe the maximum tightening torque and screw-in depth.
For additional information, contact your local Festo Service.
Profile mounting
EAHF-V2
Trunnion flange
mounting kit DAMT-V1
Direct fastening
Flange mounting
EAHH-V2
Profile
Bearing cap
Mounting via profile
Mounting via thread
Mounting via thread
Tab. 3: Overview of mounting components for bearing caps and profile
Swivel flange DAMS,
SNC..., CRSNCS
Trunnion flange ZNCF,
CRZNG
Foot mounting HNC,
CRHNC
Parallel kit
Mounting via thread
Mounting via thread
Mounting via thread
Tab. 4: Overview of mounting components for parallel kit
Size
32
40
50
63
80
100
Profile mounting EAHF-V2
Screw
Trunnion flange mounting kit DAMT-V1
Screw
M5
M6
M6
M8
M8
M8
Max. tightening torque
[Nm]
4
+1
8
+1
8
+2
18
+2
28
+2
28
+2
Direct fastening
Flange mounting EAHH-V2
Foot mounting HNC, CRHNC
Swivel flange DAMS (not ESBF-BF-32)
Trunnion flange ZNCF, CRZNG
Screw
M6
M6
M8
M8
M10
M10
Max. tightening torque
[Nm]
6
6
12
12
25
25
Max. screw-in depth t
max
[mm]
16
16
17
17
17
17
Swivel flange SNC..., CRSNCS
Screw
Tab. 5: Information for mounting components
6.5
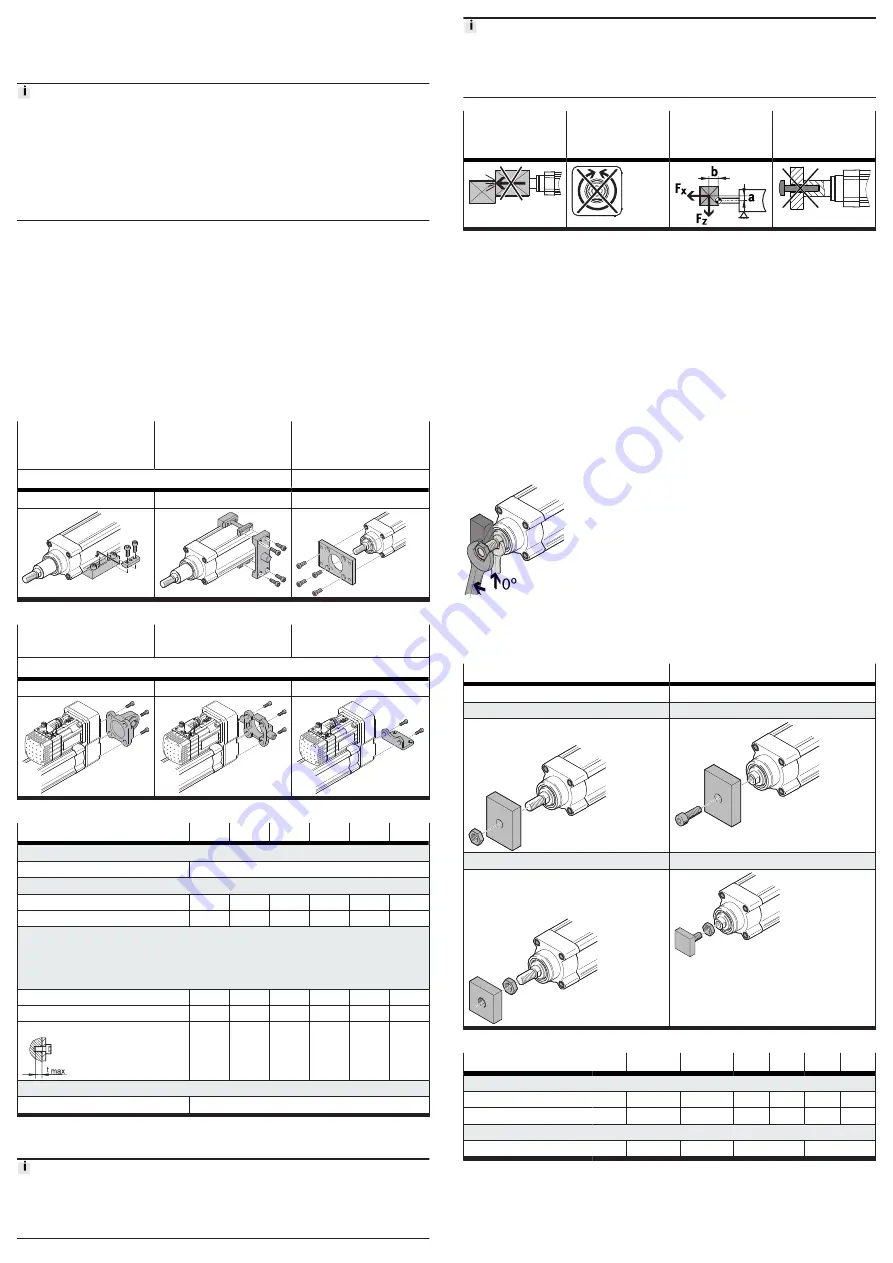
Mounting the attachment component
Torque on the Piston Rod
During commissioning and operation, the piston rod may only be operated
without torque.
If external torques occur, an external guide must be used.
Mounting the attachment component on the piston rod
When mounting the attachment component, do not exceed the maximum torque
of the piston rod. The maximum torque of the piston rod may only be used for a
short time during mounting
Tab. 8 Information on attachment components.
Collision-free
Torque-free
Centre of gravity
and tilting
moment
Max. screw-in
depth
Tab. 6: Requirement for attachment components
Requirement:
–
No collision with mounting and sensor components in the movement space of
the attachment component.
–
No transverse load or torque on the piston rod.
Absorb external forces and torques via an external guide.
–
Minimise tilting torque by the Fx and Fz forces. Short lever arms a and b from
the piston rod
to the centre of gravity of the attachment
–
The maximum screw-in depth of the retaining screws is not exceeded.
1. Select accessories
2. Screw the lock nut onto the male thread of the piston rod or attachment
component.
3. Rotate or place the attachment component on the piston rod.
4. Tighten retaining screws or lock nut.
The tightening torque must not act on the piston rod. Counterhold with a
suitable tool on the spanner flat of the piston rod.
Observe the maximum tightening torque and screw-in depth.
Fig. 2: Torque-free mounting
When using an additional external guide, ensure that the electric cylinder and
piston rod are aligned exactly parallel.
ESBF-...
ESBF-...-F
Mounting via male thread
Mounting via female thread
With nut
With screw
–
Guide unit EAGF
With lock nut
With lock nut
–
Rod eye SGS, CRSGS
–
Rod clevis SG, CRSG
–
Coupling piece KSZ
–
Self-aligning rod coupler FK; CRFK
Tab. 7: Overview of attachment components
Size
32
40
50
63
80
100
Piston rod
Width across flats
ß
[mm]
10
13
17
17
22
22
Max. torque
[Nm]
2.4
6.4
12
15
31
53
Piston rod with male thread ESBF -...
Nut, lock nut
M10x1.25
M12x1.25
M16x1.5
M20x1.5

























