2
Functional Safety Manual
M310/FSM, Rev BA
Introduction
April 2017
Introduction
1.4
Terms, abbreviations, and acronyms
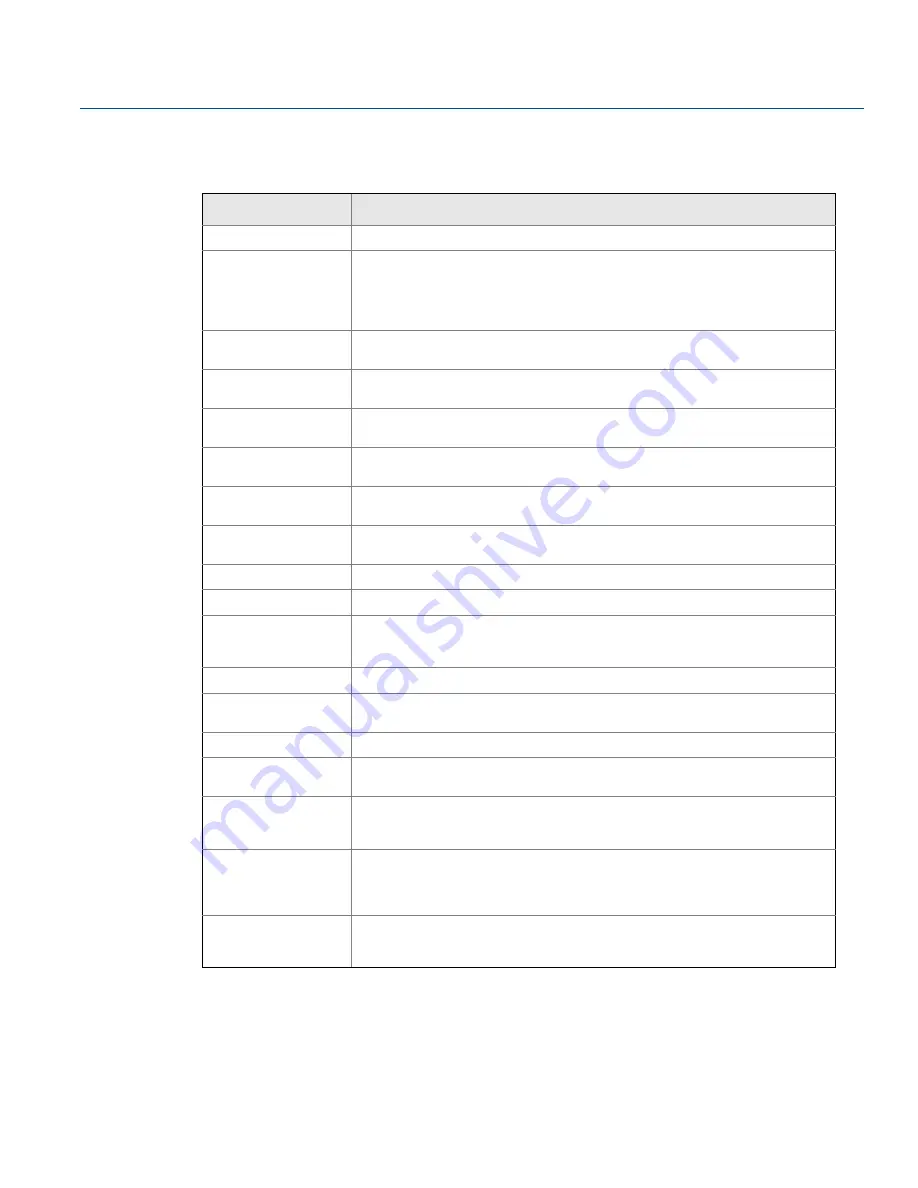
Table 1-1. Terms, Abbreviations, and Acronyms
Term
Definition
Basic safety
Freedom from unacceptable risk of harm
BPCS
Basic Process Control System – a system which responds to input signals from the
process, its associated equipment, other programmable systems and/or an
operator and generates output signals causing the process and its associated
equipment to operate in the desired manner but which does not perform any
safety instrumented functions with a claimed SIL greater than or equal to 1.
Fail Safe State
State where the switch output is in the state corresponding to an alarm
condition. In this condition, the switch contacts will normally be open.
Fail Dangerous
Failure that does not respond to an input from the process (i.e. not switching to
the fail-safe state).
Fail Dangerous
Detected
Failure that is dangerous but is detected.
Fail Dangerous
Undetected
Failure that is dangerous and that is not detected.
Fail No Effect
Failure of a component that is part of the safety function but that has no effect on
the safety function.
Fail Safe
Failure that causes the switch to go to the defined fail-safe state without an input
from the process.
FIT
FIT is the abbreviation for Failure In Time. One FIT is 1x10
-9
failure per hour
FMEDA
Failure Modes, Effects and Diagnostic Analysis
Functional Safety
Part of the overall safety relating to the process and the BPCS which depends on
the correct functioning of the Safety Instrumented System (SIS) and other
protection layers.
HFT
Hardware Fault Tolerance
Low demand
Mode of operation, where the frequency of demands for operation made on a
safety-related system is no greater than twice the proof test frequency.
PFD
AVG
Average Probability of Failure on Demand
SFF
Safe Failure Fraction – a fraction of the overall random failure rate of a device that
results in either a safe failure or a detected dangerous failure.
SIF
Safety Instrumented Function – a safety function with a specified SIL which is
necessary to achieve functional safety. Typically a set of equipment intended to
reduce the risk due to a specified hazard (a safety loop).
SIL
Safety Integrity Level - a discrete level (one out of four) for specifying the safety
integrity requirements of the safety instrumented functions to be allocated to
the safety instrumented systems. SIL 4 has the highest level of safety integrity,
and SIL 1 has the lowest level.
SIS
Safety Instrumented System (SIS) – an instrumented system used to implement
one or more safety instrumented functions. An SIS is composed of any
combination of sensors, logic solvers, and final elements.
Summary of Contents for Mobrey Series
Page 2: ......
Page 8: ...4 Functional Safety Manual M310 FSM Rev BA Introduction April 2017 Introduction ...
Page 25: ......