23
The Ω ranges are : 400.0Ω, 4.000kΩ, 40.00kΩ, 400.0kΩ, 4.000MΩ, and 40.00MΩ,
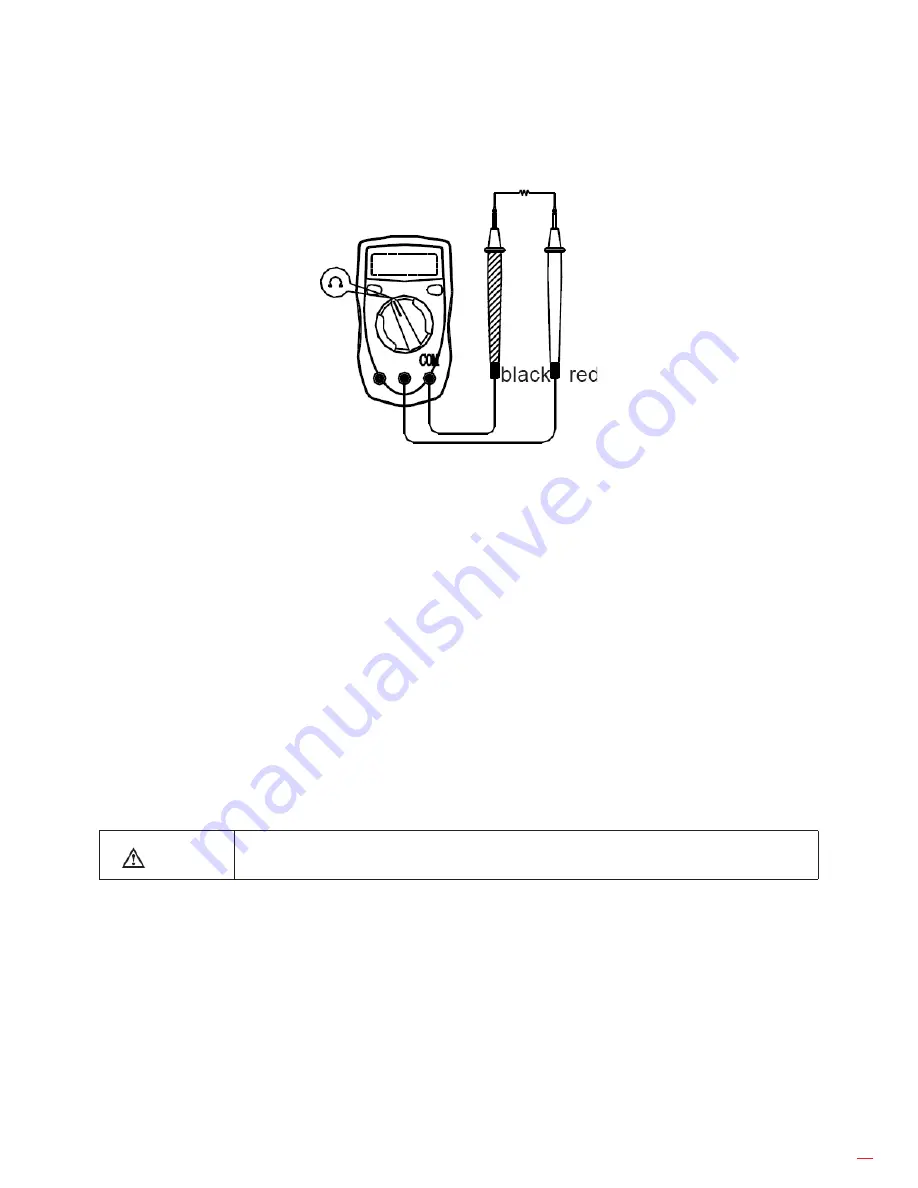
1. Insert the red test lead into the VΩmA terminal and the black test lead into the COM terminal.
2. Set the rotary switch to the Ω range.
3. Connect the test leads across with the object being measured. The measured value shows on
the display.
(figure 5)
Note:
- The test leads can add 0.1Ω to 0.3Ω of error to resistance measurement. To obtain precision
readings in low-resistance measurement, that is the range of 200Ω, short-circuit the input terminals
beforehand and record the reading obtained (called this reading as X). (X) Is the additional
resistance from the test lead. Then use the equation: measured resistance value (Y) - (X) = precision
readings of resistance.
- For high-resistance measurement (>1MΩ), it is normal taking several seconds to obtain a stable
reading.
- When resistance measurement has been completed, disconnect the connection between the
testing leads and the circuit under test.
F. Diode and Continuity Test (see figure 6)
Testing Diodes
Warning!
To avoid damages to the Meter or to the devices under test, disconnect circuit
power and discharge all the high-voltage capacitors before diodes.
Use the diode test to check diodes, transistors, and other semiconductor devices. The diode test
sends a current through the semiconductor junction, and then measures the voltage drop across
the junction.
A good silicon junction drops between 0.5V and 0.8V.
















































