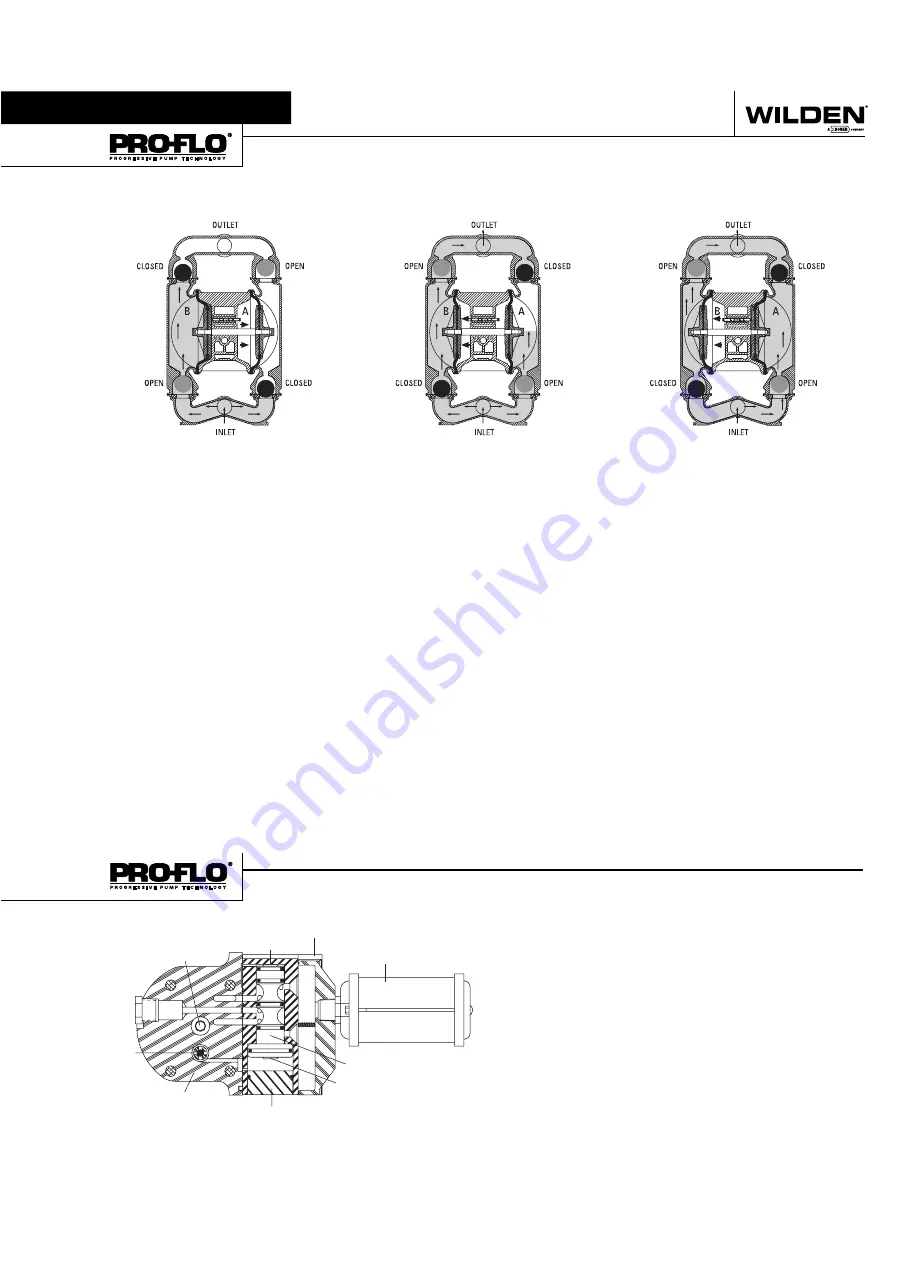
OPEN
CLOSED
OPEN
CLOSED
OUTLET
INLET
B
A
OUTLET
INLET
OPEN
CLOSED
CLOSED
OPEN
B
A
The Pro-Flo
®
patented air distribution system incorporates
three moving parts: the air valve spool, the pilot spool, and
the main shaft/diaphragm assembly. The heart of the system
is the air valve spool and air valve. As shown in Figure 1, this
valve design incorporates an unbalanced spool. The smaller
end of the spool is pressurized continuously, while the large
end is alternately pressurized and exhausted to move the
spool. The spool directs pressurized air to one chamber
while exhausting the other. The air causes the main shaft/
diaphragm assembly to shift to one side — discharging liquid on
one side and pulling liquid in on the other side. When the shaft
reaches the end of its stroke, it actuates the pilot spool, which
pressurizes and exhausts the large end of the air valve spool. The
pump then changes direction and the same process occurs in the
opposite direction, thus reciprocating the pump.
MAIN SHAFT
CENTER BLOCK
PILOT
SPOOL
SMALL END
END CAP
LARGE END
AIR VALVE SPOOL
MUFFLER
MUFFLER PLATE
The Wilden diaphragm pump is an air-operated, positive displacement, self-priming pump. These drawings show fl ow pattern through
the pump upon its initial stroke. It is assumed the pump has no fl uid in it prior to its initial stroke.
Figure 1
OUTLET
INLET
OPEN
CLOSED
CLOSED
OPEN
B
A
FIGURE 1
The air valve directs pressurized
air to the back side of diaphragm A. The
compressed air is applied directly to the
liquid column separated by elastomeric
diaphragms. The diaphragm acts as
a separation membrane between the
compressed air and liquid, balancing the
load and removing mechanical stress from
the diaphragm. The compressed air moves
the diaphragm away from the center block
of the pump. The opposite diaphragm is
pulled in by the shaft connected to the
pressurized diaphragm. Diaphragm B is on
its suction stroke; air behind the diaphragm
has been forced out to the atmosphere
through the exhaust port of the pump.
The movement of diaphragm B toward the
center block of the pump creates a vacuum
within chamber B. Atmospheric pressure
forces fl uid into the inlet manifold forcing
the inlet valve ball off its seat. Liquid is free
to move past the inlet valve ball and fi ll the
liquid chamber (see shaded area).
FIGURE 2
When the pressurized
diaphragm, diaphragm A, reaches the
limit of its discharge stroke, the air valve
redirects pressurized air to the back
side of diaphragm B. The pressurized air
forces diaphragm B away from the center
block while pulling diaphragm A to the
center block. Diaphragm B is now on its
discharge stroke. Diaphragm B forces the
inlet valve ball onto its seat due to the
hydraulic forces developed in the liquid
chamber and manifold of the pump. These
same hydraulic forces lift the discharge
valve ball off its seat, while the opposite
discharge valve ball is forced onto its seat,
forcing fl uid to fl ow through the pump
discharge. The movement of diaphragm
A toward the center block of the pump
creates a vacuum within liquid chamber A.
Atmospheric pressure forces fl uid into the
inlet manifold of the pump. The inlet valve
ball is forced off its seat allowing the fl uid
being pumped to fi ll the liquid chamber.
FIGURE 3
At completion of the stroke, the
air valve again redirects air to the back side
of diaphragm A, which starts diaphragm
B on its exhaust stroke. As the pump
reaches its original starting point, each
diaphragm has gone through one exhaust
and one discharge stroke. This constitutes
one complete pumping cycle. The pump
may take several cycles to completely
prime depending on the conditions of the
application.
Right Stroke
Mid Stroke
Left Stroke
S e c t i o n 3
H O W I T W O R K S — P U M P
H O W I T W O R K S — A I R D I S T R I B U T I O N S Y S T E M
WIL-10161-E-01
3
WILDEN PUMP & ENGINEERING, LLC




















