WIL-10252-E-01
Wilden
®
12
Suggested Installation, Operation, Maintenance and Troubleshooting
NOTE: In the event of a power failure, the shutoff valve should
be closed, if the restarting of the pump is not desirable once
power is regained.
Air-Operated Pumps: To stop the pump from operating in an
emergency situation, simply close the “shut-off” valve (user supplied)
installed in the air supply line. A properly functioning valve will stop the
air supply to the pump, therefore stopping output. This shut- off valve
should be located far enough away from the pumping equipment such
that it can be reached safely in an emergency situation
.
Operation
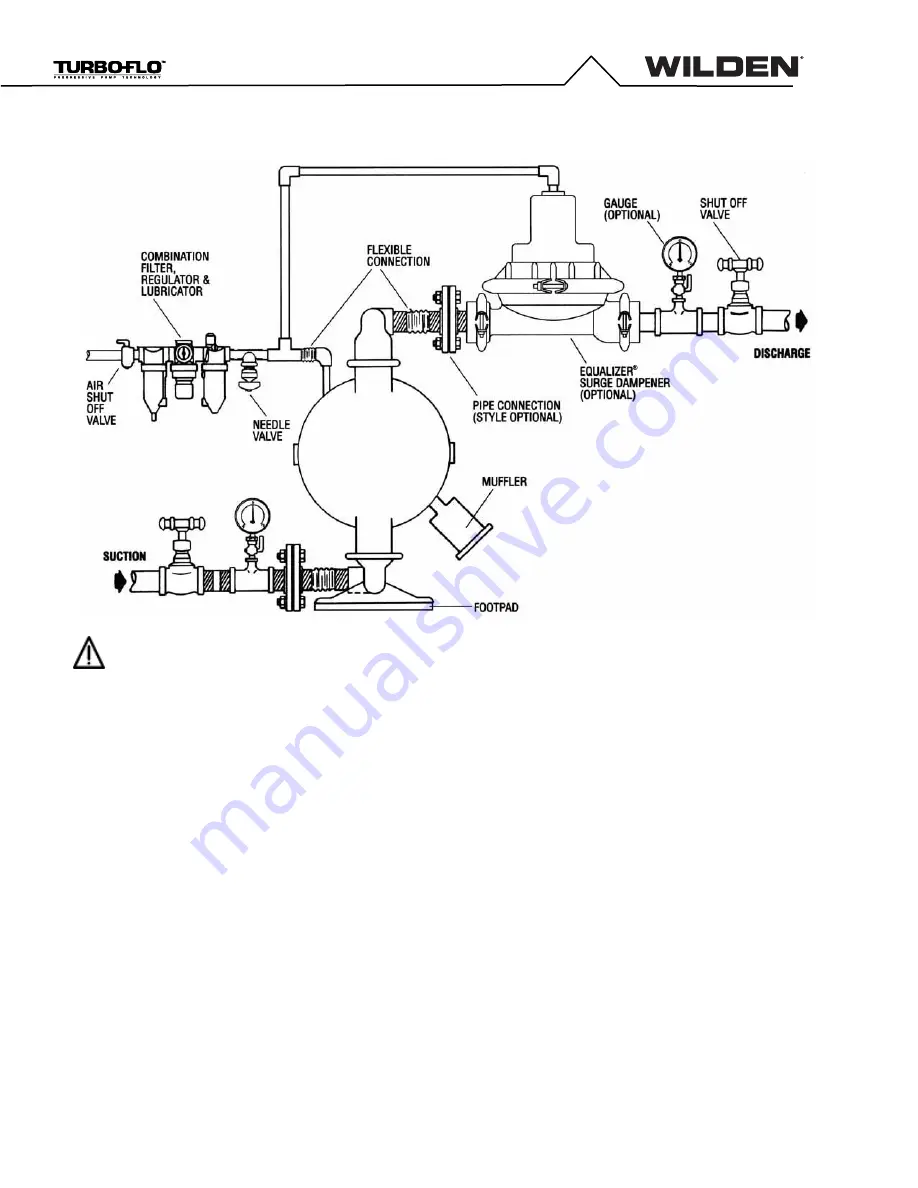
Pump discharge rate can be controlled by limiting the volume and/or
pressure of the air supply to the pump (preferred method). A regulator
is used to regulate air pressure. A needle valve is used to regulate air
volume. Pump discharge rate can also be controlled by throttling the
pump discharge by partially closing a valve in the discharge line of the
pump. This action increases friction loss which reduces flow rate. This
is useful when the need exists to control the pump from a remote
location. When the pump discharge pressure equals or exceeds the air
supply pressure, the pump will stop; no bypass or pressure relief valve
is needed, and pump damage will not occur. The pump has reached a
“deadhead” situation and can be restarted by reducing the fluid
discharge pressure or increasing the air inlet pressure. The Wilden T15
pump runs solely on compressed air and does not generate heat,
therefore your process fluid temperature will not be affected.
Maintenance and Inspections
Since each application is unique, maintenance schedules may be
different for every pump. Frequency of use, line pressure, viscosity and
abrasiveness of process fluid all affect the parts life of a Wilden pump.
Periodic inspections have been found to offer the best means for
preventing unscheduled pump downtime. Personnel familiar with the
pump’s construction and service should be informed of any
abnormalities that are detected during operation.
Records
When service is required, a record should be made of all necessary
repairs and replacements. Over a period of time, such records can
become a valuable tool for predicting and preventing future
maintenance problems and unscheduled downtime. In addition,
accurate records make it possible to identify pumps that are poorly
suited to their applications.



























