1-33
Boating Safety
The 1971 Boating Safety Act grants protection to a “Good
Samaritan” boater providing good faith assistance, and absolves a
boater from any civil liability arising from such assistance.
Hazardous Conditions
Every waterway poses hazards that should be avoided. You will be
best prepared to avoid these hazards if you are familiar with the
waterway where you are boating. Whenever possible familiarize
yourself with navigation charts, depth charts, and waterway maps
before you go boating. The following information outlines some of
the most common hazards which may be encountered:
Shallow Water Operation
Shallow water brings on obvious hazards such as sand bars,
stumps, rocks, etc. Know the area in which you will be operating
the boat. Grounding the vessel or striking submerged objects
can result in serious injury or death and can cause severe
damage to your watercraft. At high speed, this can cause rapid
deceleration or stop your boat abruptly, which may cause
occupants to impact the interior of the boat or be ejected. Stick
to deeper water whenever possible, and if you must travel in
shallow water, proceed at low speed and post a lookout.
Know the minimal depth your boat can safely travel.
Warning Markers
Learn to recognize the different buoys and day markers; they
are used as the signposts of the waterways identifying navigable
routes and water hazards. It is a good idea to ask local
authorities about hazard areas and if they are marked. Stay
within boundaries and clear of hazards.
Weeds
Weeds can generally be a threat to a boat’s engine and other
components on the boat. If weeds wrap around the propeller,
they can create vibration in the engine. They also can restrict
water intakes or clog the water filter causing the engine to
overheat. Learn to recognize the typical normal operating
temperature range for you engine. If temperature rises high
above normal, then check for blockage of the engine cooling
water system.
Super_Air_Sec 1.qxp_Nautique Ski Sec 1.qxd 7/17/17 3:21 PM Page 1-33
Summary of Contents for super air 210 2018
Page 2: ......
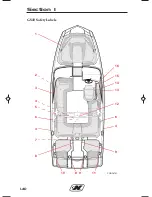
Page 50: ...1 38 GS20 Safety Labels 1 2 3 4 5 4 4 6 7 6 8 9 12 13 14 15 16 8 9 CORC0674 10 11 Section 1...
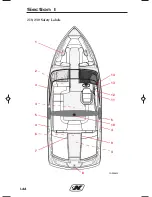
Page 52: ...1 40 GS22 Safety Labels 1 2 3 4 5 4 4 6 7 6 8 9 12 13 14 15 16 8 9 CORC0701 10 11 Section 1...
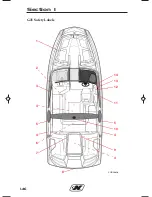
Page 54: ...1 42 GS24 Safety Labels 1 2 3 4 5 4 4 6 7 6 8 9 12 13 14 15 16 8 9 CORC0701 10 11 Section 1...
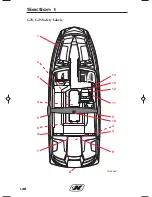
Page 56: ...1 44 210 230 Safety Labels 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 4 4 4 4 5 13 14 CORC0625 Section 1...
Page 58: ...1 46 G21 Safety Labels 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 4 4 4 4 5 13 14 CORC0626 Section 1...
Page 60: ...1 48 G23 G25 Safety Labels 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 4 4 4 4 5 13 14 CORC0627 Section 1...
Page 109: ...2 5 NOTES GS20 GS22 GS24 G21 G23 G25 210 and 230...
Page 128: ...2 24 Section 2 210 Seating Area Designated Occupant Positions 12 CORC0612...
Page 132: ...2 28 Section 2 230 Seating Area Designated Occupant Positions 15 CORC0613...
Page 134: ...2 30 Section 2 G23 Seating Area Designated Occupant Positions 16 CORC0615...
Page 139: ...3 3 Controls and Indicators CORC143...
Page 166: ...3 30 Section 3 230 G21 G23 and G25 A CORC0505 T HANDLE T HANDLE A CORC0450...
Page 184: ...3 48 NOTES Section 3...
Page 188: ...4 4 Fuel System G21 G23 G25 Section 4...
Page 197: ...4 13 Boat Systems Port and Starboard Ballast Bags G21 G23 G25...
Page 204: ...4 20 NOTES Section 4...
Page 228: ...6 8 Section 6 NOTES...
Page 252: ...8 4 Section 8 NOTES...
Page 274: ...W 8 NOTES...
Page 275: ......
Page 276: ......