Operational Theory
Xenus XTL User Guide
22
Copley Controls Corp.
2.5.4: Position Mode and Position Loop
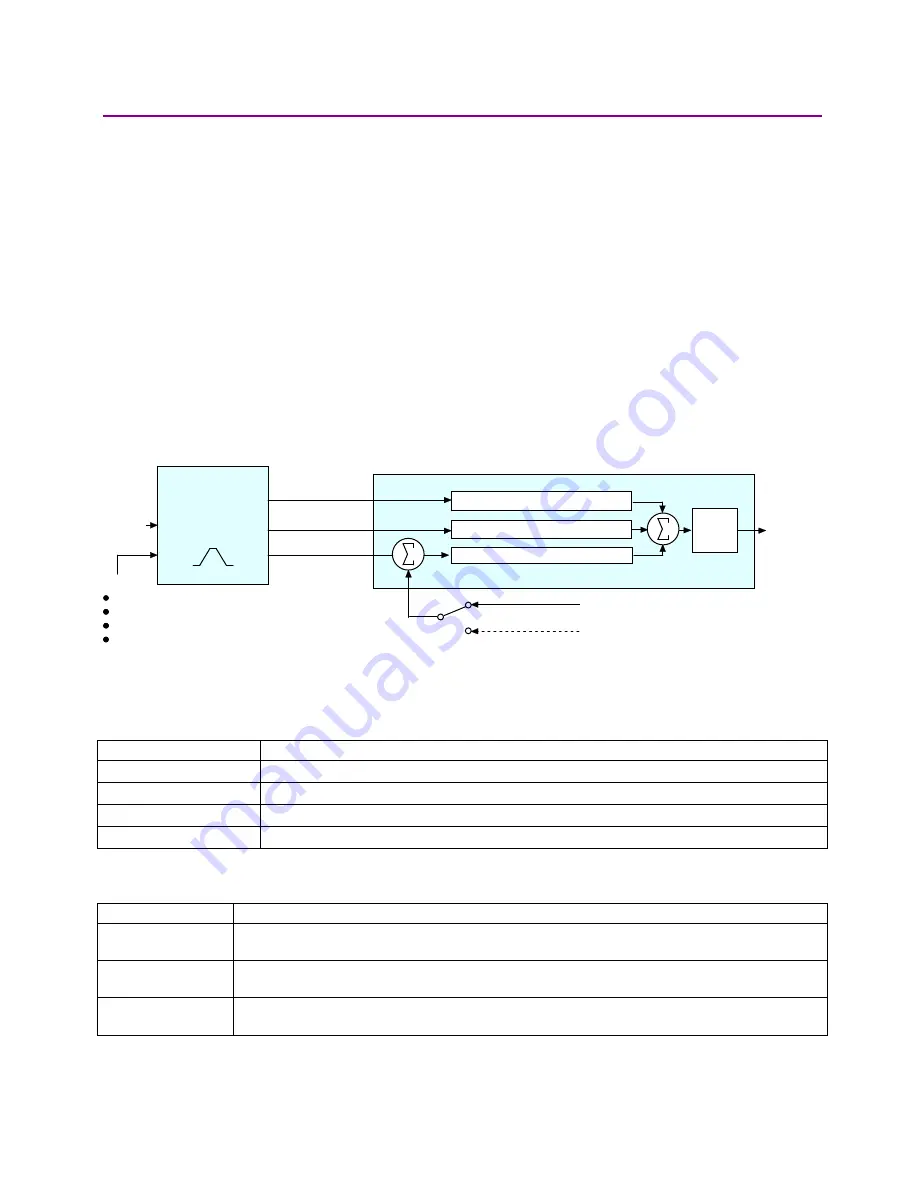
Position Loop Diagram
The amplifier receives position commands from the digital or analog command inputs, over the
CAN interface or serial bus, or from the CVM Control Program. When using digital or analog
inputs, the amplifier's internal trajectory generator calculates a trapezoidal motion profile based on
trajectory limit parameters. When using the CAN bus, serial bus, or CVM Control Program, a
trapezoidal or S-curve profile can be programmed. The trajectory generator updates the
calculated profile in real time as position commands are received.
The output of the generator is an instantaneous position command (limited position). In addition,
values for the instantaneous profile velocity and acceleration are generated. These signals, along
with the actual position feedback, are processed by the position loop to generate a velocity
command.
To bypass the trajectory generator while in digital or analog position modes, set the maximum
acceleration to zero. The only limits in effect will now be the velocity loop velocity limit and the
current limits. (Note that leaving the maximum acceleration set to zero will prevent other position
modes from operating correctly.)
The following diagram summarizes the position loop.
Target
Position
Velocity
Command
Trajectory
Ge ne rator
Position Loop
Feedback
Limits:
Max velocity
Max accel
Max decel
Abort decel
Position Proportional Gain (Pp)
Velocity Feed Forw ard (Vff)
Acceleration Feed Forw ard (Aff)
Profile Acceleration
Profile Velocity
Limited Position
+
+
-
+
+
Gain
Multiplier
from motor encoder or resolver
from optional position encoder (on load)
Trajectory Limits
In position mode, the trajectory generator applies the following user-set limits to generate the
motion profile.
Limiter Description
Maximum Velocity
Limits the maximum speed of the profile.
Maximum Acceleration
Limits the maximum acceleration rate of the profile.
Maximum Deceleration
Limits the maximum deceleration rate of the profile.
Abort Deceleration
Specifies the deceleration rate used by the trajectory generator when motion is aborted.
Position Loop Inputs From the Trajectory Generator
The position loop receives the following inputs from the trajectory generator.
Input Description
Profile Velocity
The instantaneous velocity value of the profile. Used to calculate the velocity feed forward
value.
Profile Acceleration The instantaneous acceleration/deceleration value of the profile. Used to calculate the
acceleration feed forward value.
Limited Position
The instantaneous commanded position of the profile. Used with the actual position feedback to
generate a position error.
Summary of Contents for Xenus XTL
Page 1: ...Xenus XTL User Guide P N 95 00875 000 Revision 3 June 2008...
Page 2: ...Xenus XTL User Guide This page for notes...
Page 8: ...About this Manual Xenus XTL User Guide 8 Copley Controls Corp This page for notes...
Page 12: ...Introduction Xenus XTL User Guide 12 Copley Controls Corp...
Page 51: ...Xenus XTL User Guide Specifications Copley Controls Corp 51 3 24 Dimensions...
Page 52: ...Specifications Xenus XTL User Guide 52 Copley Controls Corp...
Page 72: ...Wiring Xenus XTL User Guide 72 Copley Controls Corp...
Page 158: ...Regen Resistor Sizing and Configuration Xenus XTL User Guide 158 Copley Controls Corp...
Page 172: ...Xenus Filter Xenus XTL User Guide 172 Copley Controls Corp...






























