8
P/N: 192090087 REV. AA
October 2021
MAINTENANCE
INSPECTION
To maintain continuous and satisfactory operation, regularly
inspect the unit and replace worn or damaged parts before they
become unsafe. Determine the intervals of inspection based on
the individual application and also the type of service to which the
hoist is subjected. The intervals indicated as follows are based on
normal service.
Divide inspections into two general classifications (frequent and
periodic).
FREQUENT INSPECTIONS
The operator conducts these visual examinations daily or before
each use, including:
1.
Braking mechanism for evidence of slippage.
2.
Operation of the directional lever for free movement.
3.
Load chain for lubricant, wear, damaged links or foreign
material.
4.
Hooks for damage, cracks, twists, latch engagement and latch
operation.
PERIODIC INSPECTIONS
A designated person conducts visual inspections of external
and internal conditions, making records to provide the basis for
continuing evaluation of the condition of the hoist. Determine the
frequency of periodic inspections based upon usage as defined in
ASME B30.21. Periodic inspections should include those items as
well as the following:
1.
Chain for excessive wear or stretch
(See Figures 7 thru 8, starting on page 8).
2.
Worn, cracked or distorted parts such as lower hook block,
upper hook block, upper hook pin, chain guide, bushings,
lever, brake cover, free-chaining knob, directional pawl, friction
hub and lever ratchet.
3.
Inspect for wear on the tip of the pawls, teeth of the ratchet,
and pockets of the lift-wheel.
4.
Loose or missing bolts, nuts, pins or rivets.
5.
Inspect the brake components for worn, glazed or
contaminated friction discs and scoring of the friction hub and
ratchet. Replace brake ratchet assembly if contaminated,
glazed or if thickness is less than the following thickness:
• 0.256 in. (6.5 mm) for 3/4-ton and 1-1/2-ton units
• 0.307 in. (7.8 mm) for 3-ton and 6-ton units
6.
Corroded, stretched or broken pawl springs, directional lever
pawl spring and lever ratchet spring.
7.
Hooks – Visual inspection based upon ASME B30.10 and
ASME B30.21.
8.
Nameplate and warning labels for legibility and retention.
9.
Chain stop in place and properly secured.
Correct any deficiency before returning the hoist to service. Also,
the external conditions may show the need for more detailed
inspection which, in turn, may require the use of non-destructive
type testing.
Replace any parts deemed unserviceable, using new parts before
returning the hoist to service. Destroy unserviceable parts and
properly dispose of them to prevent any future use of them.
When the unit is subjected to heavy usage or dusty, gritty, moist
or corrosive atmospheric conditions, assign shorter time periods
between inspections. Inspect all parts for unusual wear, corrosion or
damage, in addition to those specifically mentioned in the schedule.
HOOK INSPECTION
Replace hooks that have suffered damage from chemicals,
deformations or cracks, or that have a twist from the plane of
the unbent hook, excessive opening or seat wear (see ASME
B30.10). Also, replace hooks that are opened to the extent that
the latch does not engage the tip. Any hook that is twisted or has
excessive throat opening indicates abuse or overloading of the
hoist. Inspect other load-sustaining parts for damage.
Check to assure the latch is not damaged or bent and that
it operates properly. The latch should have sufficient spring
pressure to keep it tightly against the tip of the hook and allow it to
spring back to the tip when released. Replace the latch if it does
not operate properly.
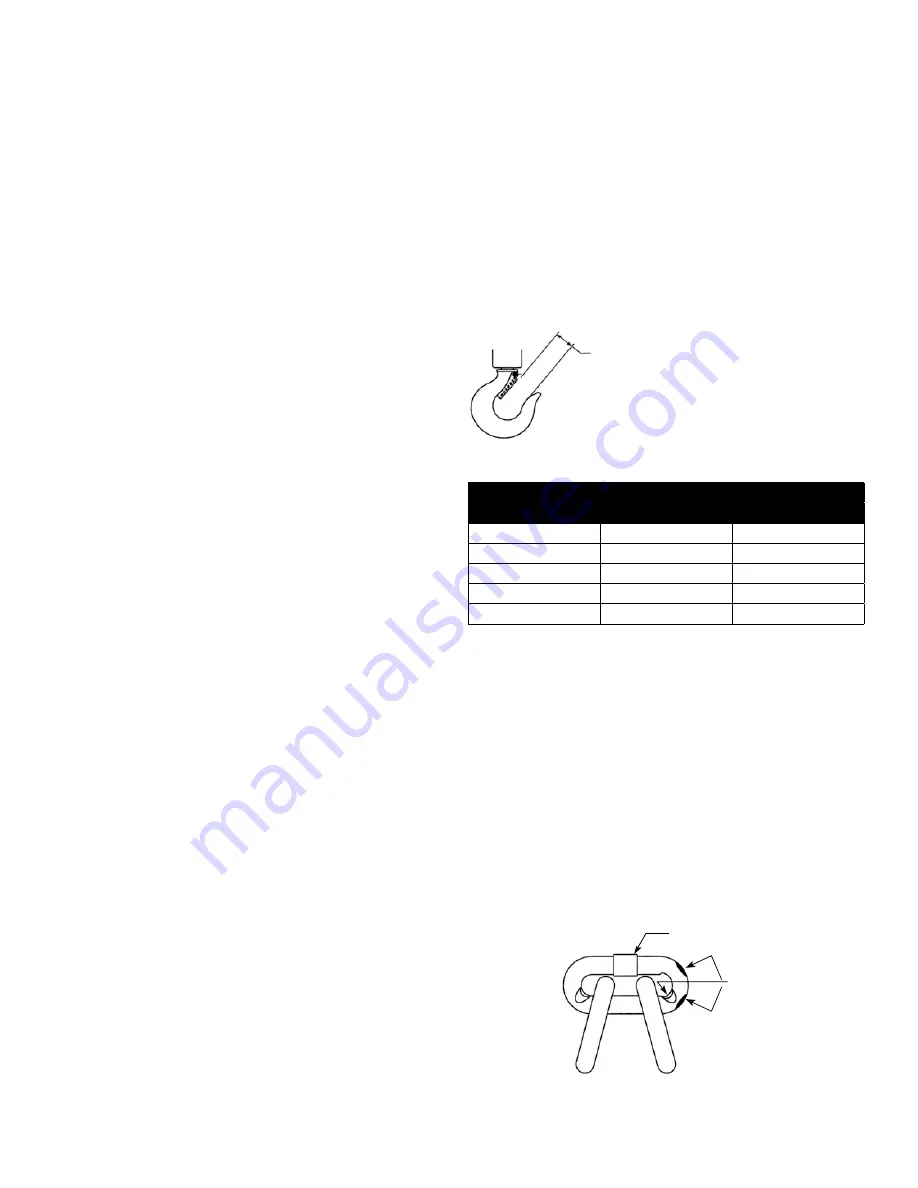
Use the chart below Figure 6 to determine when the hook needs
replacing.
Depress latch to
measure throat
opening
Figure 6: Hook Inspection
Rated Load
Standard Throat Opening
(lb)
(Ton)
in. (mm)
1500
3/4
1.10 (21)
2000
1
1.25 (22)
3000
1-1/2
1.37 (26)
6000
3
1.44 (31)
12000
6
2.00 (46)
Table 2: Hook Replacement
NOTE: Hook should be frequently inspected to ensure that
any distortion causing an increase to throat opening does
not exceed 10%.
LOAD CHAIN
The chain should feed smoothly into and away from the hoist. If
the chain binds, jumps or produces noise, first clean and lubricate
it (See Chain Lubrication on Page 9). If trouble persists, inspect
the chain and mating parts for wear, distortion or other damage.
CHAIN INSPECTION
First clean the chain with a non-caustic/non-acid type solvent
and conduct a link-by-link inspection for nicks, gouges, twisted
links, weld spatter, corrosion pits, striations (minute parallel lines),
cracks in weld areas, wear and stretching. Replace the chain if it
has any one of the defects shown in Figure 7.
Weld
Wear
in
these
areas
Figure 7: Chain Inspection