8
English
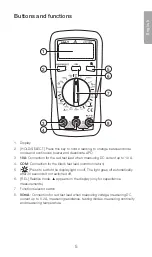
1. Set the function selector to
NCV
, “EF” will appear on
the display.
2. Hold the top of the multimeter (marked “NCV” with an arrow
on top) close to the test subject.
3. The voltage will be represented by a number of dashes “-”
on the display:
“
EF
”
0–50 mV
“
−
”
50–100 mV
“
− −
”
100–150 mV
“
− − −
”
150–200 mV
“
− − − −
”
> 200 mV
Battery test
• When “Bad” appears on the display, the battery
needs to be replaced.
• If the battery is under 0.2 V, only a flashing
“Good”, “Low” or “Bad” will be displayed.
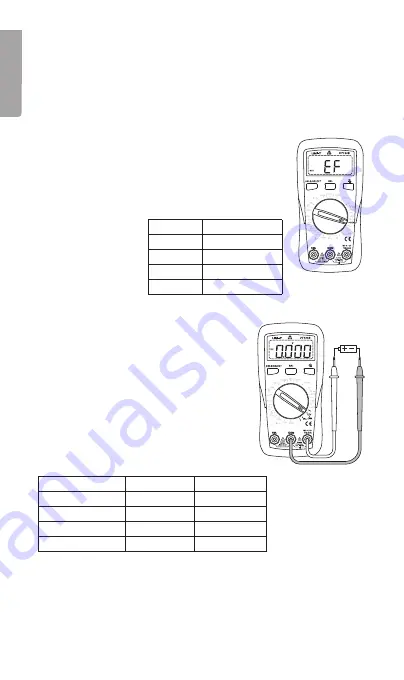
1. Connect the black test lead to
COM
and the red
lead to
VΩmA
.
2. Set the function selector to
9 V
or
1.5 V
depending
on the type of battery you wish to test.
3. The status of the tested battery is described on
the display as either “Good”, “Low” or “Bad”:
Battery model
1.5 V
9 V
Load resistance
30
Ω
900
Ω
Good
≥ 1.31 V
≥ 7.8 V
Low
0.95–1.31 V
5.7–7.7 V
Bad
≤ 0.94 V
≤ 5.6 V
The table only provides
an approximate value,
for more exact values
it is recommended that
the test leads be used.
• If there are several cables with 2-phase or 3-phase cables close to one another,
try to separate them and measure each cable individually.
• Electrical cables consist of 2 or more conductors and only some of the conductors
might be carrying current at the time of the measurement. Therefore, always
measure all conductors in a cable to get a correct value.
• The NCV function only works when measuring AC (alternating current), not DC
(direct current).