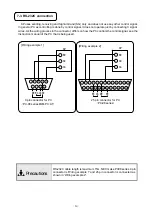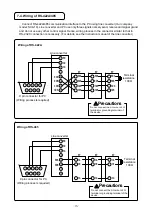
- 18 -
8-2. Data time interval
During RTU mode: Less than 9600bps = 20msec, 9600bps or more = 5msec
During ASCII mode: Less than 1 second
When sending a message, do not let the time interval of data that makes up one message exceed
the time span mentioned above. If it exceeds the time interval mentioned above, the receiving side
(this device), in order to judge the end of transmission from the transmission side, processes it as an
abnormal message reception.
In RTU mode message characters should be sent continuously whereas in ASCII mode as
character gap is maximum 1 second, master (PC) processing speed is comparatively slow but it can
be used.
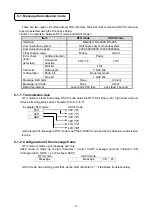
8-3. Message configuration
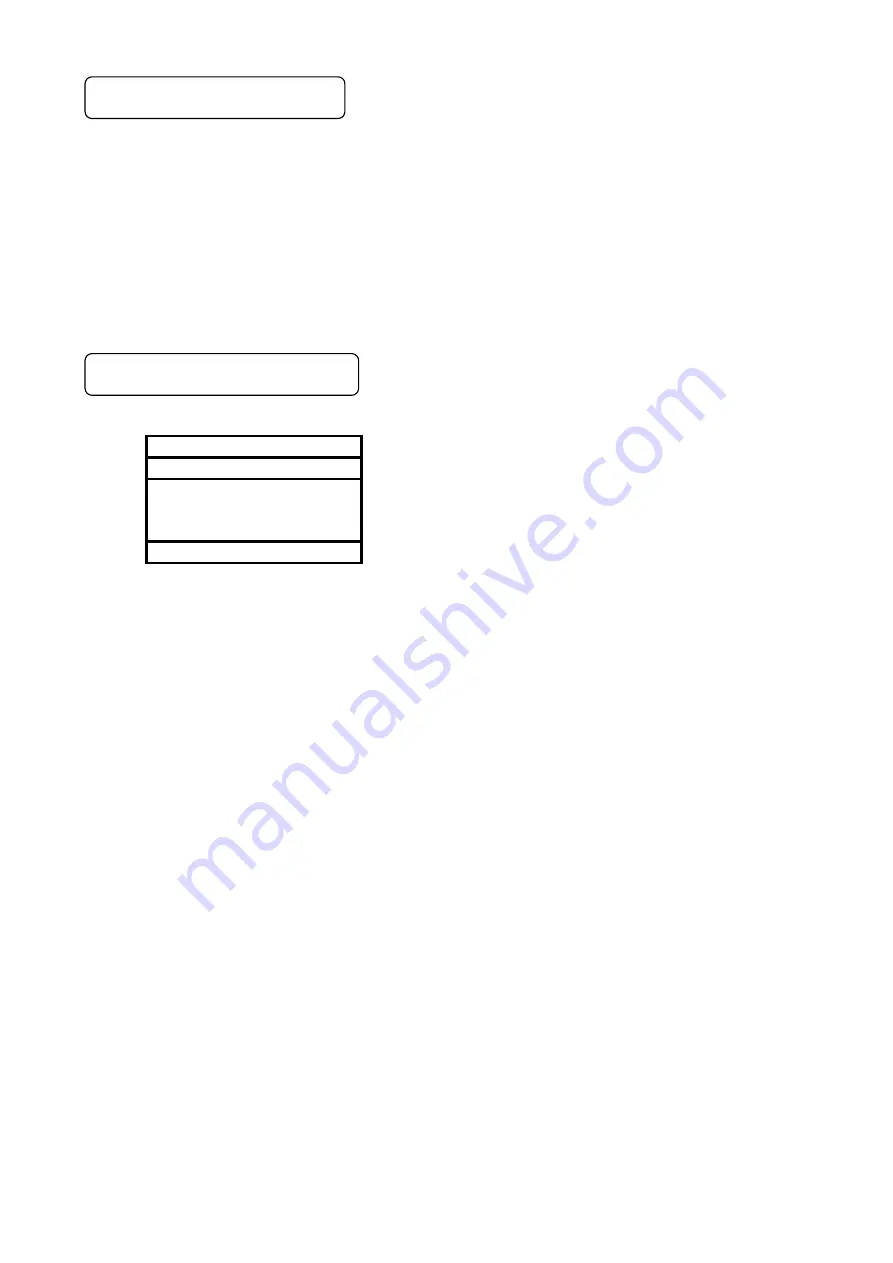
MODBUS message is made up of the following, in case of both the RTU and ASCII mode.
Slave address
Function code
Data
Error check
8-3-1. Slave address
Set the slave address beforehand in a range of 1 to 99 using front key setting. Master usually does
the transmission with one slave. All the connected devices receive in common the message sent
from the master. However, the slave whose slave address matches with the slave address in the
command message only responds to that message.
Slave address '0' is used in message (broad cast) for all the slaves from the master. In this case the
slave does not return a response.
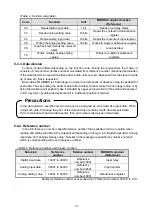
8-3-2. Function code
Function code is a code that is to be executed in the slave and each data is roughly categorized as
follows. For details, see the reference table.
①
Digital input data
: DI input status etc.
②
Analog setting value
: Various setting information. Numeric value range is a numeric value
within the range of 16 bits.
-32768 to 32767 (For details see reference table).
③
Analog input data
: Measurement data, status etc. Numeric value range is a numeric value
within a range of 16 bits.