MIDI
E-51
MIDI
The letters MIDI stand for Musical Instrument Digital
Interface, which is the name of a worldwide standard for
digital signals and connectors that makes it possible to
exchange musical data between musical instruments and
computers (machines) produced by different manufacturers.
MIDI compatible equipment can exchange keyboard key
press, key release, tone change, and other data as messages.
Though you do not need any special knowledge about MIDI
to use this keyboard as a stand-alone unit, MIDI operations
require a bit of specialized knowledge. This section provides
you with an overview of MIDI that will help to get you going.
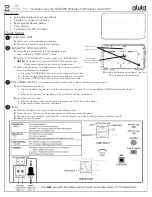
MIDI messages are send out through the MIDI OUT terminal
of one machine to the MIDI IN terminal of another machine
over a MIDI cable. To send a message from this keyboard to
another machine, for example, you must use a MIDI cable to
connect the MIDI OUT terminal of this keyboard to the MIDI
IN terminal of the other machine. To send MIDI messages
back to this keyboard, you need to use a MIDI cable to connect
the other machine’s MIDI OUT terminal to the MIDI IN
terminal of this keyboard.
To use a computer or other MIDI device to record and
playback the MIDI data produced by this keyboard, you must
connect the MIDI IN and MIDI OUT terminals of both
machines in order to send and receive data.
1
Computer or other MIDI device
To use the MIDI THRU function of a connected computer,
sequencer, or other MIDI device, be sure to turn this
keyboard’s LOCAL CONTROL off (page E-54).
MIDI allows you to send the data for multiple parts at the
same time, with each part being sent over a separate MIDI
channel. There are 16 MIDI channels, numbered 1 through 16,
and MIDI channel data is always included whenever you
exchange data (key press, pedal operation, etc.).
Both the sending machine and the receiving machine must be
set to the same channel for the receiving unit to correctly
receive and play data. If the receiving machine is set to
Channel 2, for example, it receives only MIDI Channel 2 data,
and all other channels are ignored.
1
MODE
2
TRANSPOSE/TUNE/MIDI
3
Number buttons
4
START/STOP
5
LEFT/TRACK 1
6
RIGHT/TRACK 2
7
[+]/[–]
What is MIDI?
MIDI Connections
MIDI Channels
641A-E-053A
Summary of Contents for LK-73
Page 14: ...641A E 130A...
Page 16: ...Appendix Ap ndice A 2 641A E 132A...
Page 18: ...Appendix Ap ndice A 4 Fingered Chord Chart Cuadro de acordes Fingered 641A E 134A...
Page 19: ...A 5 Appendix Ap ndice 641A E 135A...
Page 20: ...Appendix Ap ndice A 6 Rhythm List Lista de ritmos 641A E 136A...
Page 21: ...641A E 137A...
Page 22: ...641A E 138A...
Page 23: ...641A E 139A...
Page 24: ......