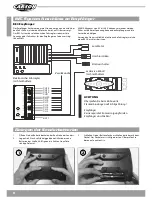
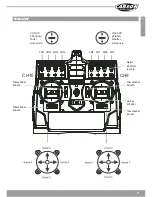
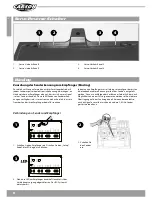
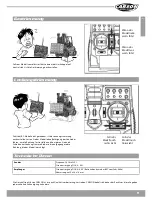
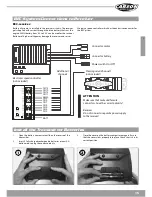
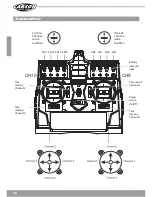
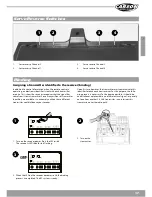
13
Features of the 2.4 GHz Remote Controls
The transmitter technology at 2.4 GHz is fundamentally different
in some aspects from the technology in the 27.35 and 40 MHz
frequency ranges, which up to now have been conventional with
remote control models. The previous style of location using a
channel determined by plug-in crystals is gone, and the transmitter
and receiver work with encoding. The receiver accepts only signals
with the coding from its own transmitter. Each signal from the
transmitter lasts just milliseconds. Before the next signal, a pause is
inserted, which lasts longer than the transmission signal.
Nonetheless, within each second countless signals are received and
evaluated by the receiver. Signals that the receiver recognizes as
defective (false encoding, strings that don’t fit the signal schema,
etc.) are suppressed and are not passed on as control commands.
And as the frequency gets higher, the antennas get shorter.
Remote controls using this transmitter technology or model
construction are not subject to fees.
Advantages of the 2.4 GHz Technology
Worth Noting
Although the frequency range used is also divided into channels,
the user doesn’t have to worry about their configuration and has
no influence on it anyway.
Because the same encoding is used by the transmitter and receiver,
interruption by another receiver or a different transmitter will not
occur.
Plug-in crystals are not needed, because the transmitter creates
the currently appropriate frequency using a synthesizer circuit,
as does the receiver, which determines the right frequency for ist
encoding.
The old fear of double occupancy of a channel (as when a second
transmitter overreaches and interrupts a receiver) is a thing of the
past. An operator can go ahead and switch on a transmitter and
receiver, without negotiating with other model users.
The data transfer capacity is considerably larger than that of
previous remote controls, which has a positive effect on control of
the digital servo, for example.
Best of all, at events with a lot of participants, you can always use
your own equipment for settings, tests and conversions, because
the number of active transmitters is almost unlimited.
At very low wavelengths, obstacles can weaken or interrupt the
spread of radio waves. That means there should be as few obstacles
as possible in the line between the transmission and reception
antennas.
The model’s receiver antenna must be as far away as possible from
electrically conductive parts and very visibly arranged (protruding
from the model) to prevent loss of range.
Summary of Contents for reflex stick multi pro
Page 26: ...26 Notizen Notes ...
Page 27: ...27 ...