Appendix B. Installation Scenarios
B-7
Radio ID
4094
2
2
3
3
11, 12 etc.
3
21, 22, etc
3
Notes:
1
your
Network ID
and
Frequency Key
may be different
2
to match
LoggerNet
PakBus address
3
to match CR1000 PakBus address
4
not inclusive; other typical hardware items may include power supply, antenna, enclosure, etc.
NA = not applicable
B.4 Example 4: Phone-to-RF Base
In this example, a COM220 phone modem and master radio are connected
without a datalogger to a network of CR1000s in the field (see FIGURE
and TABLE
). The computer running
LoggerNet
uses a phone modem to
call into the master site and connect to the rest of the network. The rest of the
network can be configured as in other examples. In this configuration,
datalogger-to-datalogger communications and datalogger call-back is NOT
supported; see Example 5.
Phone
Modem
Slave 2
Slave 1
PC Running
LoggerNet
/PC400
Phone
to RF451
Base
FIGURE B-8. Schematic of Phone-to-RF Base
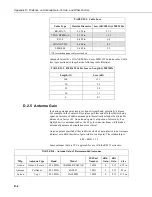
TABLE B-4. RF451 Settings for Example 4
Phone to RF451 Base
Slaves
Hardware
3
PC running
LoggerNet
, Phone Modem
COM220,
RF451, A100
CR1000, RF451
Active Interface
ME Master
Auto-Sense
Baud Rate
115.2K
115.2K
Radio Operation
Mode
Multi-Point Master
Multi-Point Slave
Network ID
1
1726
1726
Frequency Key
1
1
1
Radio ID
2
3
2
Notes:
1
your
Network ID
and
Frequency Key
may be different
2
to match CR1000 PakBus address
3
not inclusive; other typical hardware items may include power supply, antenna, enclosure, etc.
Summary of Contents for RF451
Page 2: ......
Page 6: ......
Page 10: ...Table of Contents iv ...
Page 34: ...RF451 Spread Spectrum Radio 24 ...
Page 36: ......
Page 46: ...Appendix B Installation Scenarios B 10 ...
Page 58: ...Appendix D Distance vs Antenna Gain Terrain and Other Factors D 10 ...
Page 60: ......
Page 61: ......