14
7. Adjusting the angle
Angular position transmitters of the KINAX WT 717 range do not require
a mechanical zero position mark (however, this is made if required by the
customer, see Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Left:
for rotation transmitters with the range of 0 to ...
º,
Right:
for rotation transmitters with V characteristic ranges.
Fig. 2.
Sense of rotation seen from the shaft side:
Left: counterclockwise, right: clockwise.
During installation the shaft of the transmitter can be coupled to the object
to be measured in any position. Adjust the shaft angle as follows with the
2W2 configuration software:
1. Remove the cover (3.1 in Fig. 4). Remove the rubber cover (5.1) to gain
access the programming connector (5), (see section “8.1 Connecting
transmitter”). Connect the KINAX WT 717 to the programming device
according to Fig. 3. Start the 2W2 configuration software. If necessary,
configure the device with the required measuring range data.
The angular position transmitter must only be programmed
outside of the Ex area!
2. Place the measuring device in a defined position (prefereably the zero
position).
3. Select the
“Adjustment”
menu item under
“SERVICE”
in the configuration
software. In the
“Mechanical position”
window enter the current angle
of the measuring device and then select
“Adjust”.
The measuring device
is now configured for the defined angle.
Programming
connector
Interface
KINAX WT717
PK 610
Ancillary cable
OFF
ON
OFF: Power supply
by measuring output
(Fig. 5)
ON: Power supply
provided by PC
Fig. 3. Connection diagram programming
If you programm the KINAX WT717 with a connected power
supply, then the switch on the interface PK610 must be im
-
perative switched to OFF. If this is ignored, this can lead to the
destruction of the device.
8. Electrical connections
Screw terminals
and
cable glands
are provided for making the electrical
connections to the transmitter.
Note that, …
… the data required to carry out the prescribed measurement
must correspond to those marked on the nameplate of the
KINAX WT 717 (measuring) input, measuring output, power
supply)!
… the total loop resistance connected to the output (receiver
plus leads)
does not
exceed the maxi mum permissible value
R
ext.
! See
“Measuring output”
, section “5. Technical data”!
… twisted cores must be use for the measured variable input
and output leads and routed as far away as possible from
power cables!
In all other respects, observe all local regulations when selecting
the type of electrical cable and installing them!
In the case of
“Intrinsically safe”
explosion-proof versions,
the supplementary information given on the EC-Type-
Examination Certificate, the EN 60 079-14 and also local
regulations applicable to electrical installations in explosion
hazard areas must be taken into account!
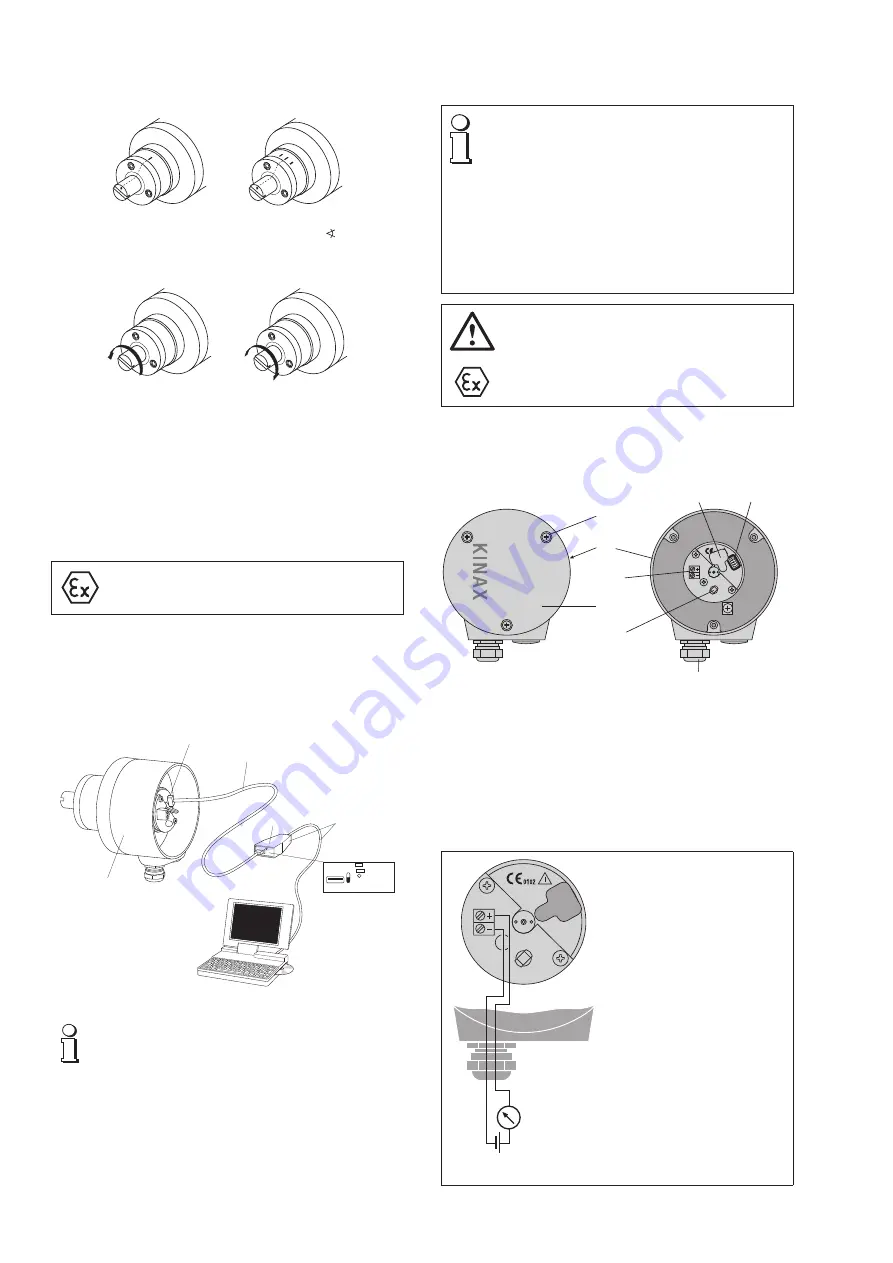
8.1 Connecting transmitter
To connect the transmitter, first remove the 3 screws (3.2), and remove the
cover (3.1). The maximum wire gauge the terminals (4.1) can accept is 1.5 mm
2
.
(3.2)
(3.1)
(3)
(4)
(4.1)
(4.2)
(5)
(5.1)
Fig. 4. Rear (3) with terminals (4.1) and cable glands (4).
Left:
with cover (3.1) closed.
Right:
without cover (3.1).
Undo the gland nut and remove the pinch ring and seal from the gland opening.
Place these parts over the cable in the correct order and pass the end of the
cable through the gland hole into the rear of the transmitter.
Strip the insulation from a suitable length of the leads and connect them to
the terminals (4.1) according to Fig. 5.
Then fit the gland seal, pinch ring and nut. Tighten the gland nut and replace
the cover.
R
ext
– +
+
–
H
H =
DC
power supply
H = 12…33 V
resp. H = 12…
30
V with
Ex
version
R
ext
= External resistance
Fig. 5. Connection diagram.
























