Principle of DP vacuum pumps
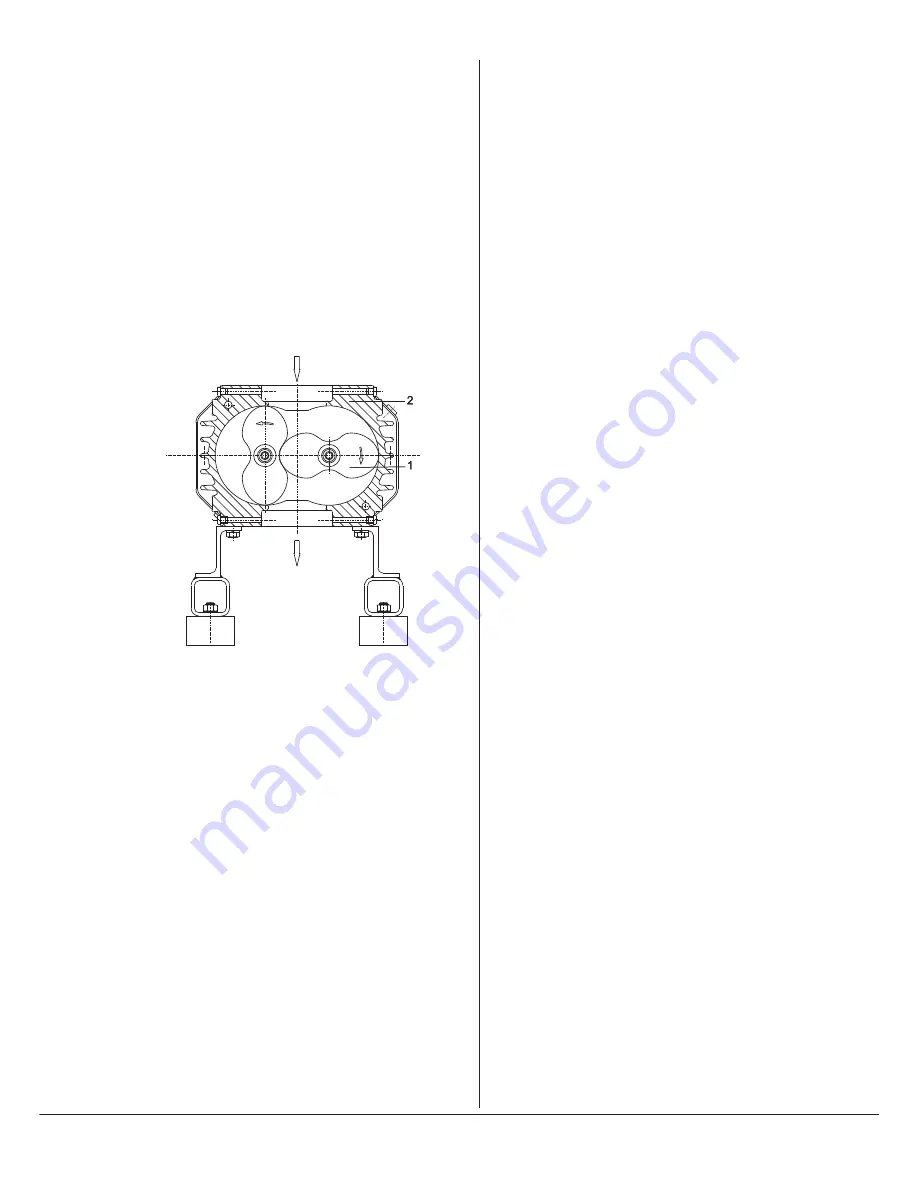
The COBRA NW screw vacuum pumps work by the principle of spiral
pumps. Two parallel screws (8) rotate in opposite directions in the
pump body. Entering gases are trapped between the flights of the
screws and the pump body. The gases are conveyed by the rotation of
the screws to the exhaust, where they are discharged.
The COBRA NW screw vacuum pumps are driven by water-cooled mo-
tors.
Principle of MB vacuum pumps
The Roots vacuum pumps operate according to the approved principle
of the Roots type machine. Operation is both simple and effective.
Two lobes (9) with identical profiles rotate in opposition directions wi-
thin a casing. As they rotate, gas is drawn into the space between each
lobe and the casing where it is trapped and by the rotation pushed out
into the discharge. This action is repeated twice for each revolution of
each lobe and therefore four times for each revolution of the drive
shaft. There is no mechanical contact between lobes and cylinder. So
no oil lubrication is required.
The drive motor of roots pump is a water cooled canned motor.
Gas flow checks
A pressure sensor PSA at the discharge monitors the discharge pres-
sure. If the pressure reaches more than the limit value (alarm, preset at
the factory: 0.2 bar), the purge cycle starts.
Oil circuit
Since the complete operating principle works without contact, no oil
circuit is needed in the work area.
Cooling
The vacuum pump is cooled by
–
a direct cooling water circuit in the motors and the DP and MB
transmission casing . The flow regulating valve CWR of cooling
water is preset on 2 l/min at the factory.
–
a direct cooling water circuit in the rear bearing (for exceptionally
cool running in option).
NOTE
: The COBRA BC 0600 F vacuum pumps are principally dispat-
ched without oil already in the vacuum pump but, without cooling wa-
ter. Before vacuum pump first startup, control the oil level and the
cooling liquid level. In the event of absence of one or the other of
these lubricants, please carry out the filling (please refer to the various
chapters of filling). Do not forget to connect the cooling water supply
before the first startup. Operation without these coolants can result in
damage to the vacuum pump.
Nitrogen system
The nitrogen system can be used in a number of different ways :
–
nitrogen is used as dilution gas. It is injected inside the cylinder on two
different places. Nitrogen flow injected in the middle hole is preset at 2
l/ min and can be adjusted with valve DGR 1, depending on the appli-
cation. Nitrogen flow injected in the hole on cylinder endplate side is
preset at 10 l/ min and can be adjusted with valve DGR 2, depending
on the application. When flow is too low a warning then an alarm signal
is generated by flowmeter DGF to the PLC. Status of the pump depends
on the alarm function set by user (factory setting : None, pump conti-
nues running with an alarm). Dilution improves the screws functioning,
especially when sucking corrosive gases.
–
nitrogen is used as sealing gas. The nitrogen is injected between
the transmission and the process gas to achieve good closeness.
The Nitrogen flow used for the sealing is set by two chips (
f
). With
a pressure of 1,5 bar, the flow is around 8-10 l/min.
–
nitrogen is used as purge gas. The purge eliminates traces of gases
remaining in the vacuum pump. The vacuum pump purge cycle is
programmed in the control and starts, either after a STOP opera-
tion or after an alarm function.
For a correct purge execution, the shut-off valve at the inlet flange
must be closed. The purge cycle lasts about 30 min. (Program-
mable time in the basic parameters).
Optional functions/ Use of available
accessories
A pressure sensor (PSA) mounted at the exhaust , controls the over-
pressure at the exhaust. If overpressure is above 0,3 bar, pressure
sensor gives a warning then an alarm signal. Status of the pump de-
pends on the alarm function set by user (factory setting : None, pump
continues running with an alarm).
A temperature sensor PT100 (TSA) mounted on the cylinder, measures
the temperature inside the cylinder (DP).
A silencer or sound absorber (accessory) at the exhaust reduces the
noise of the pump and collects any condensate.
A leak-protection non-return valve (optional) at the exhaust traps the
condensate in the pump when the pump is switched off.
The LCD controller processes the data of the sensors as follows:
–
PSA: exhaust pressure
–
TSA: temperature inside the cylinder DP
–
MOT 1 and MOT 2: DP and MB current and speed
–
DGF: nitrogen flow rate, dilution
–
CWM: cooling water flow rate in motors/ transmission
See "Installation and Maintenance Instructions, Busch PLC and Busch
LCD (No. 0870758077)".
On/ Off switch
The vacuum pump is delivered with a circuit breaker. The function
start/ stop can be done in Local by using the LCD controller or in Re-
mote by the production machine.
Versions
Further vacuum pump descriptions state the nominal displacement and
the design level.
Example: BC 0600 F
BC = standard version
0600 = 600 m
3
/h
F = Design
BC 0600 F
Product description
0870767449 (En)
Page 7