8
HEAT PUMP REFRIGERATION
SYSTEM
UNIT OPERATION AND SAFETY HAZARD
Failure to follow this warning could cause personal
injury, death and/or equipment damage.
This system uses Puron
R
refrigerant which has
higher pressures than R--22 and other refrigerants. No
other refrigerant may be used in this system. Gauge
set, hoses, and recovery system must be designed to
handle Puron refrigerant. If unsure about equipment,
consult the equipment manufacturer.
!
WARNING
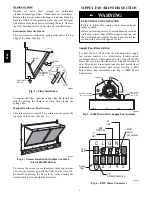
Outdoor Coil
The 548J outdoor coil is fabricated with round tube
copper hairpins and plate fins of various materials and/or
coatings (see “Appendix I -- Model Number Significance”
to identify the materials provided in this unit). All unit
sizes use composite--type two--row coils. Composite
two--row coils are two single--row coils fabricated with a
single return bend end tubesheet.
Indoor Coil
The indoor coil is traditional round--tube, plate--fin
technology. Tube and fin construction is of various
optional materials and coatings (see Model Number
Format). Coils are multiple--row.
Outdoor Coil Maintenance and Cleaning
Recommendation
Routine cleaning of coil surfaces is essential to maintain
proper operation of the unit. Elimination of contamination
and removal of harmful residues will greatly increase the
life of the coil and extend the life of the unit. The
following maintenance and cleaning procedures are
recommended as part of the routine maintenance activities
to extend the life of the coil.
Remove Surface Loaded Fibers
Surface loaded fibers or dirt should be removed with a
vacuum cleaner. If a vacuum cleaner is not available, a
soft non--metallic bristle brush may be used. In either
case, the tool should be applied in the direction of the fins.
Coil surfaces can be easily damaged (fin edges can be
easily bent over and damage the coating of a protected
coil) if the tool is applied across the fins.
NOTE
: Use of a water stream, such as a garden hose,
against a surface loaded coil will drive the fibers and dirt
into the coil. This will make cleaning efforts more
difficult. Surface loaded fibers must be completely
removed prior to using low velocity clean water rinse.
Periodic Clean Water Rinse
A periodic clean water rinse is very beneficial for coils
that are applied in coastal or industrial environments.
However, it is very important that the water rinse is made
with very low velocity water stream to avoid damaging
the fin edges. Monthly cleaning as described below is
recommended.
PERSONAL INJURY AND UNIT DAMAGE
HAZARD
Failure to follow this caution may result in personal
injury or equipment damage.
Only approved cleaning is recommended.
CAUTION
!
Routine Cleaning of Indoor Coil Surfaces
Periodic cleaning with Totaline
®
environmentally sound
coil cleaner is essential to extend the life of coils. This
cleaner is available from our Replacement Components
Division as part number P902--0301 for one gallon
container, and part number P902--0305 for a 5 gallon
container. It is recommended that all coils, including
standard
aluminum,
pre--coated,
copper/copper or
E--coated
coils
be
cleaned
with
the
Totaline
environmentally sound coil cleaner as described below.
Coil cleaning should be part of the unit’s regularly
scheduled maintenance procedures to ensure long life of
the coil. Failure to clean the coils may result in reduced
durability in the environment.
Avoid the use of
S
coil brighteners
S
acid cleaning prior to painting
S
high pressure washers
S
poor quality water for cleaning
Totaline
environmentally
sound
coil
cleaner
is
nonflammable, hypoallergenic, non bacterial, and a
USDA accepted biodegradable agent that will not harm
the coil or surrounding components such as electrical
wiring, painted metal surfaces, or insulation. Use of
non--recommended coil cleaners is strongly discouraged
since coil and unit durability could be affected.
Clean coil as follows:
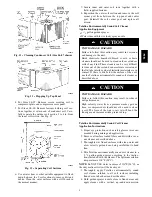
1. Turn off unit power, tag disconnect.
2. Remove top panel screws on outdoor coil end of unit.
3. Remove coil corner post. See Fig. 11. To hold top
panel open, place coil corner post between top panel
and center post. See Fig. 12.
548J