Bosch Rexroth AG
, RE 92202/02.2015
4
A7VO Series 63
| Axial piston variable pump
Hydraulic fluids
Hydraulic fluids
The A7VO variable pump is designed for operation with HLP
mineral oil according to DIN 51524.
Application instructions and requirements for hydraulic
fluids should be taken from the following data sheets
before the start of project planning:
▶ 90220: Hydraulic fluids based on mineral oils and
related hydrocarbons
▶ 90221: Environmentally acceptable hydraulic fluids
▶ 90222: Fire-resistant, water-free hydraulic fluids
(HFDR/HFDU)
▶ 90223: Fire-resistant, water-containing hydraulic fluids
(HFC, HFB, HFAE, HFAS)
Details regarding the selection of hydraulic fluid
The hydraulic fluid should be selected such that the
operating viscosity in the operating temperature range is
within the optimum range (
ν
opt
, see selection diagram).
Note
At no point of the component may the temperature be
higher than 115 °C. The temperature difference specified in
the table is to be taken into account when determining the
viscosity in the bearing.
If it is not possible to maintain the conditions above due to
extreme operating parameters, we recommend flushing the
case at port
U.
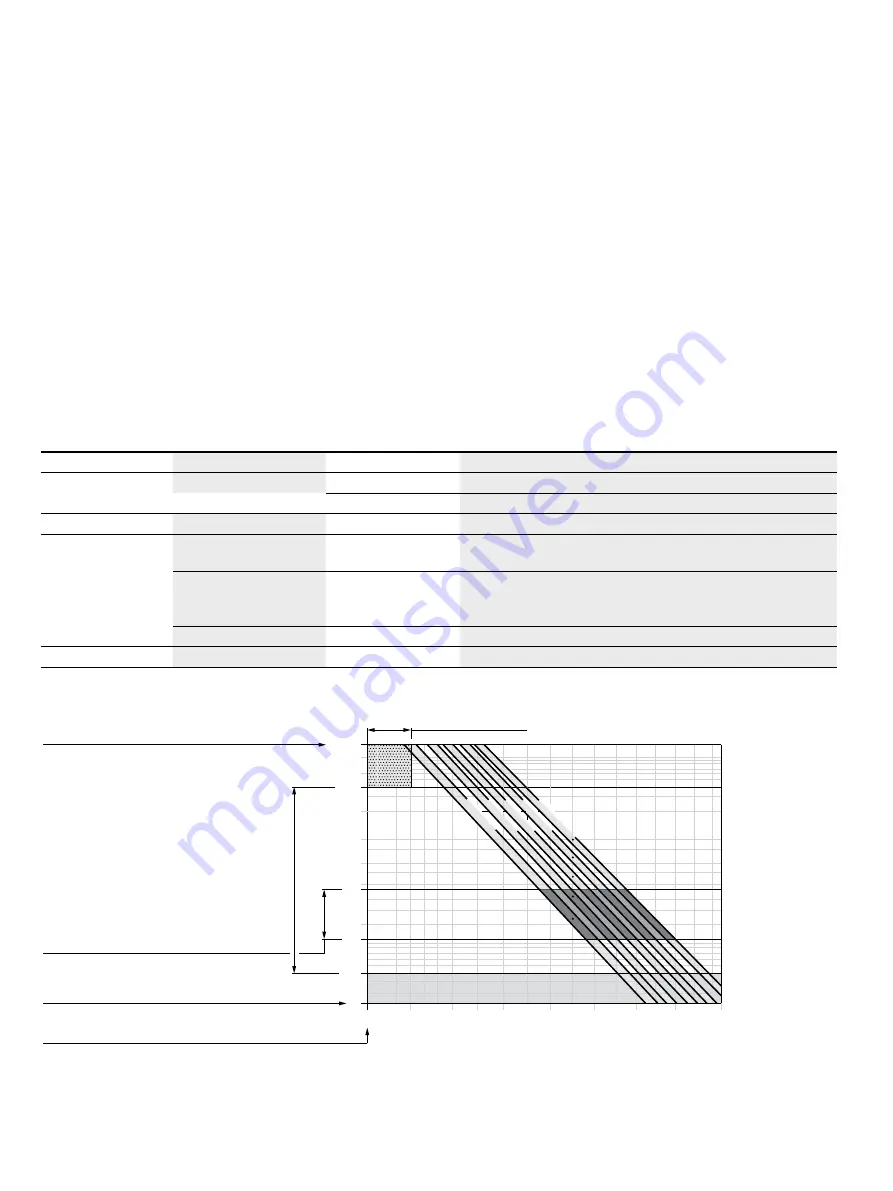
Viscosity and temperature of hydraulic fluids
Viscosity
Temperature
Comment
Cold start
ν
max
≤ 1600 mm
2
/s
θ
St
≥ -40 °C
t
≤ 3 min,
n
≤ 1000 rpm, without load
p
≤ 50 bar
Permissible temperature difference
ΔT
≤ 25 K
between axial piston unit and hydraulic fluid in the system
Warm-up phase
ν
< 1600 to 400 mm
2
/s
θ
= -40 °C to -25 °C
at
p
≤ 0.7 ×
p
nom
,
n
≤ 0.5 ×
n
nom
and
t
≤ 15 min
Continuous operation
ν
= 400 to 10 mm
2
/s
This corresponds, for example on the VG 46, to a temperature
range of +5 °C to +85 °C (see selection diagram)
θ
= -25 °C to +103 °C
measured at port
R
1
/
R
2
Note the permissible temperature range of the shaft seal
(
ΔT
= approx. 12 K between the bearing/shaft seal and port
R
1
/
R
2
)
ν
opt
= 36 to 16 mm
2
/s
Range of optimum operating viscosity and efficiency
Short-term operation
ν
min
≥ 7 mm
2
/s
t
< 3 min,
p
< 0.3 ×
p
nom
▼ Selection diagram
-40
-25
-10
10
30
50
90
115
70
0
7
10
40
60
20
100
200
400
600
1000
1600
VG 22VG 32VG 46VG 68VG 100
16
36
Range of optimum operating viscosity
v
opt
Optimum efficiency
Maximum permissible viscosity for cold start
Minimum permissible viscosity for short-term operation
Temperature
θ
[°C]
Viscosity
v
[mm
2
/s]
Continuous oper
ation
Warm-up phase
Minimum permissible temperature for cold start



















