21
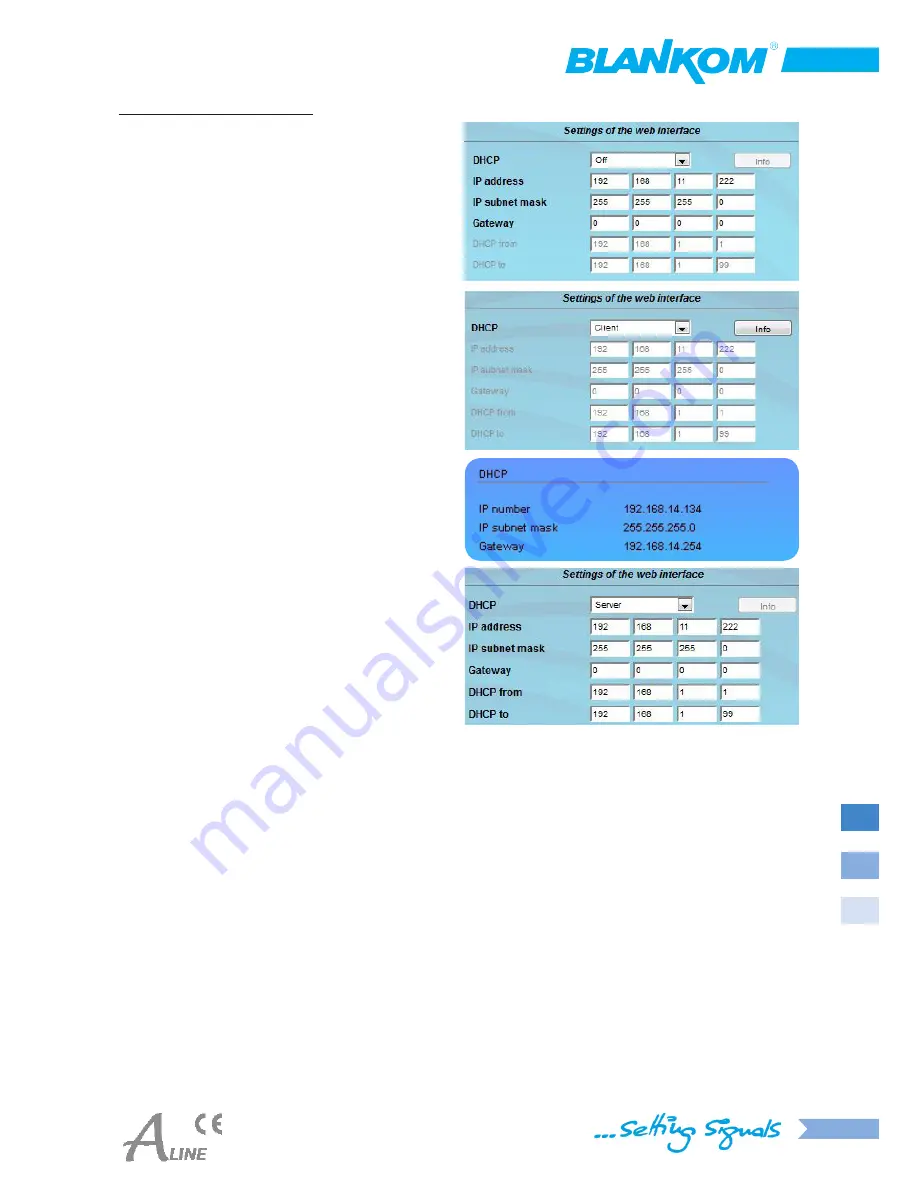
Settings of the web interface
The device supports the DHCP functionality. DHCP-Client
is factory default. Note, that after each factory reset the
device is set to “
DHCP-Client
“.
If the
DHCP functionality
is set to “
Off
“, the appropriate
fields for IP number, subnet mask and gateway can be set
manually to fit the network.
If the device is set as “
DHCP-Client
“, it automatically obtains
an IP address from the DHCP server on the network. The
manual network settings are disabled.
By pressing the “
Info
“ button the automatically assigned
network configuration of the device is displayed. Close the
window by clicking in its lower area or wait 20 seconds.
Please note:
If the device is set as “
DHCP-Server
“, the IP address
192.168.1.100
must not
be set. If you select this address
an error message will be displayed.
In addition to the IP settings, you can configure the DHCP
range from which the connected client IP addresses are
assigned. The address range has to match the IP address
and subnet mask of the server and should not be too small.
The default is 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.99.
Along with the DHCP server a local DNS (Domain Name Server) will be set up. To use it in full extent a connected PC/
laptop must be configured as a DHCP client. Note that, using Windows, not only the IP address but also the DNS server
address has to be obtained automatically.
If the device is configured as a DHCP server or client and the client has received an IP address successfully, the device
can be accessed via a web browser using its name. This name is composed of the prefix “sbl“ and the device number
that is printed on the back of the device and on the packaging. For example, the device with the number 0123456 can
be found under “sbl0123456“. It might be necessary to add the domain name. In case that the device was configured
as a server, the name of the domain is “sbl0123456.sbl“. If another DHCP server is used, ask your administrator for the
domain name.
An example for the simplification of the configuration or operation of the headend via DHCP is, that an A-LINE-SBL device
is configured as a server, the remaining devices and the connected PC/ laptop are configured as a client.
By calling “dhcp.sbl“ in the browser the GUI of the server device is loaded. Now the headend can be read. So all connected
components are found and listed. The headend can now be stored in the
Setup→System administration
. By selecting the
respective devices link in the headend overview, you can switch to the other devices user interface quickly.






























