www.balluff.com
BIS V-6108 PROFINET
Processor Unit
85
english
7
Device Functions
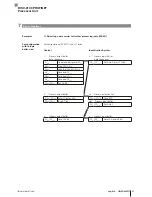
13. Bulk Read (only BIS VU)
Read from all data carriers that are located in front of the antenna. Read 4 bytes starting at data
carrier address 3.
Control
Identification System
1.
Process output buffer
(note sequence):
2.
Process Input Buffer
(note sequence):
01
hex
Command designator 53
hex
00
hex
/0F
hex
Set AA bit
02
hex
Start address 03
hex
01
hex
Enter the number of tags
03
hex
Start address 00
hex
02
hex
Enter the number of bytes
per tag
04
hex
No. of bytes 04
hex
05
hex
No. of bytes 00
hex
03
hex
…0E
hex
Enter 12 bytes of data and
the check byte
06
hex
Subset Type 00
hex
07
hex
Max Tags FF
hex
00
hex
/0F
hex
Invert TO bit
00
hex
/0F
hex
Set AV Bit
00
hex
/0F
hex
Set AE bit
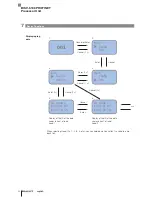
3a. Process input buffer:
01
hex
Copy the number of tags
02
hex
Copy the number of bytes
per tag
03
hex
…06
hex
Copy the 4th byte of data
for the 1st tag
07
hex
Read the check byte
08
hex
…0b
hex
Copy the 4th byte of data
for the 2nd tag
0C
hex
Read the check byte
0D
hex
/0E
hex
Copy the 2nd byte of data
for the 3rd tag
3b. Process output buffer:
4.
Process input buffer:
00
hex
/0F
hex
Invert TI bit
01
hex
…08
hex
Enter l8 bytes of data and
the check byte
00
hex
/0F
hex
Invert TO bit
00
hex
/0F
hex
Set AE bit
5a. Process input buffer:
6a. Process input buffer:
01
hex
…02
hex
Copy the 2nd byte of data
for the 3rd tag
00
hex
/0F
hex
Reset AA and AE bits
03
hex
Read the check byte
04
hex
…07
hex
Copy the 4th byte of data
for the 4th tag
08
hex
Read the check byte
5b. Process output buffer:
00
hex
/0F
hex
Reset AV bit
Examples