Section 3
Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Maintenance & Troubleshooting 3-1
MN605
General Inspection
Inspect the motor at regular intervals, approximately every 500 hours of operation or every 3
months, whichever occurs first. Keep the motor clean and the ventilation openings clear. The following
steps should be performed at each inspection:
1. Check that the motor is clean. Check that the interior and exterior of the motor is free of dirt, oil,
grease, water, etc. Oily vapor, paper pulp, textile lint, etc. can accumulate and block motor
ventilation. If the motor is not properly ventilated, overheating can occur and cause early motor
failure.
2. Periodically measure the motor winding resistance to ensure that the integrity of the winding
insulation has been maintained. Record the motor winding resistance. Immediately investigate any
significant drop in insulation resistance.
3. Check all electrical connectors to be sure that they are tight.
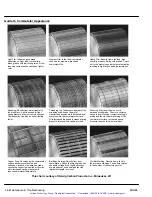
4. Check for too much vibration or looseness. It may be caused by improper alignment, an unbalanced
coupling sheave, damaged motor bearings, or loose mounting bolts. Excessive vibration will damage
the motor bearings, brushes and commutator.
5. Listen for unusual noises, especially in the area of the bearings. Also, rubbing or rumbling noises
could be signs of internal damage. Check for loose parts on the motor such as thru bolts, hold down
bolts, bad alignment of hoods, etc. An unbalanced armature or load may also cause noise.
Note: Motors applied with rectified power supplies will often make a humming noise when operating
normally. This is even more noticeable at lower operating speeds. If you can hear a growling or
erratic hum, the power supply should be checked for proper operation and phase balance.
Improper adjustment or functioning of the power supply can cause overheating of the motor and
shorten its life.
6. At start
−
up, check the tightness of the main and commutating pole bolts (external on the frame) as
listed in Table 3-1. Loose pole bolts could be a source of unpleasant noise when rectified power runs
the motor.
Table 3-1 Torque Specifications for Commutating and Main Pole Bolts
Frame
Bolt Size
Torque (lb-ft)
180AT
3/8 - 16
24 - 30
210AT
3/8 - 16
24 - 30
250AT
3/8 - 16
24 - 30
280AT
1/2 - 13
60 - 75
320AT
1/2 - 13
60 - 75
360AT
3/8 - 16
24 - 30
400AT
3/8 - 16
24 - 30
500AT
1/2 - 13
60 - 75
Artisan Technology Group - Quality Instrumentation ... Guaranteed | (888) 88-SOURCE | www.artisantg.com