Chapter 2 – Before you begin
19
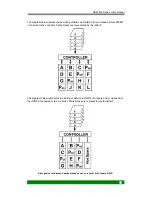
RAID 5 and RAID 5+hot spare
RAID 5 uses a mathematical expression that compares data from three drives and calculates
a fourth piece of data called “parity” which is saved on a fourth drive. Should one of the drives
fail, parity data can be used to rebuild the failed data. Under RAID 5, parity data is stored
across all drives in the array. This maximizes the amount of storage capacity available from all
drives in the array while still providing data redundancy. RAID 5 requires at least three drives.
The allows users to set RAID 5 with three drives and the fourth drive as a “hot spare” ready to
be used for rebuilding data in case one of the other drives fails. This is RAID 5 +hot spare
function.
RAID 5: Independent data disks with distributed parity blocks
Characteristics: Recommended
use:
Each entire data block is written on a data disk.
Parity for blocks in the same rank is generated
on Writes, recorded in a distributed location and
checked on Reads.
Highest Read data transaction, medium Write
data transaction rate.
Relatively low ratio of ECC (Parity) disks to data
disks means high efficiency (compared to other
RAID levels).
Good aggregate transfer rate.
Storage capacity = (No. of disks – 1) ×
(capacity of smallest disk)
In RAID 5, installed drives each are 40 GB, 50
GB, 60 GB, 70 GB, the RAID capacity will be 120
GB.
In RAID 5 + hot spare, installed 40 GB, 50 GB, 60
GB each in disk 2, 3, 4 and installed 70 GB in
disk 1 as hot spare disk, the RAID capacity will
be 80 GB.
File and application
servers
Database
servers
WWW, E-mail and News
servers
Intranet
servers
Most versatile Raid level