ATtiny22/22L
39
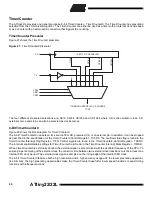
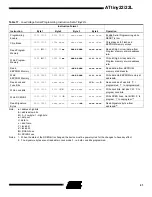
Low-Voltage Serial Programming Algorithm
When writing serial data to the ATtiny22/L, data is clocked on the rising edge of SCK.
When reading data from the ATtiny22/L, data is clocked on the falling edge of SCK. See Figure 34, Figure 35 and Table 18
for timing details.
To program and verify the ATtiny22/L in the Low-Voltage Serial Programming mode, the following sequence is recom-
mended (see four byte instruction formats in Table 17 ):
1.
Power-up sequence:
Apply power between V
CC
and GND while RESET and SCK are set to “0” (if the programmer can not guarantee that
SCK is held low during power-up, RESET must be given a positive pulse after SCK has been set to “0”). If the device is
programmed for external clocking, apply a 0 to 8 MHz clock to the PB3 pin. If the internal RC oscillator is selected as
the clock source, no external clock source needs to be applied.
2.
Wait for at least 20 ms and enable serial programming by sending the Programming Enable serial instruction to the
MOSI (PB0) pin. Refer to the above section for minimum low and high periods for the serial clock input, SCK.
3.
The serial programming instructions will not work if the communication is out of synchronization. When in sync, the
second byte ($53) will echo back when issuing the third byte of the Programming Enable instruction. Whether the
echo is correct or not, all 4 bytes of the instruction must be transmitted. If the $53 did not echo back, give SCK a
positive pulse and issue a new Programming Enable instruction. If the $53 is not seen within 32 attempts, there is
no functional device connected.
4.
If a Chip Erase is performed (must be done to erase the Flash), wait t
WD_ERASE
after the instruction, give RESET a
positive pulse, and start over from Step 2. See Table 19 on page 42 for t
WD_ERASE
value.
5.
The Flash or EEPROM array is programmed one byte at a time by supplying the address and data together with the
appropriate Write instruction. An EEPROM memory location is first automatically erased before new data is written.
Use Data Polling to detect when the next byte in the Flash or EEPROM can be written. If polling is not used, wait
t
WD_PROG
before transmitting the next instruction. See Table 20 on page 42 for t
WD_PROG
value. In an erased device,
no $FFs in the data file(s) needs to be programmed.
6.
Any memory location can be verified by using the Read instruction which returns the content at the selected
address at the serial output MISO (PB1) pin.
7.
At the end of the programming session, RESET can be set high to commence normal operation.
8.
Power-off sequence (if needed):
Set CLOCK/XTAL1 to “0”.
Set RESET to “1”.
Turn V
CC
power off.