Product Overview
Set-Top Entertainment Hub DCX3600-M
•
User Guide
11
365-095-25659 x.1
Fi interface that allows it to be connected to the wireless home network. However, it is
important to note that the ability to share content with other devices
2.4 GHz Wireless Routers
directly on the capabilities of the wireless router itself. This will be discussed further below.
There are a number of wireless networking standards in use today for both commercial and
residential applications. The majority of these wireless networks operate within the 2.4 GHz
frequency band, the 5 GHz frequency band, or both. The first widely-available wireless
networking devices available to the public were designed to meet the IEEE 802.11b wireless
standard. The 802.11b standard works entirely within the 2.4 GHz frequency band, but since its
maximum data transfer rate is only 11 MBps, its available bandwidth is unable to support any of
the advanced content sharing capabilities of the DCX3600-M. If the home is equipped with an
802.11b wireless router, it must be upgraded to an 802.11g (or better) wireless router in order
to make full use of the content sharing capabilities of the DCX3600-M.
The IEEE 802.11g wireless standard defined the next generation of wireless networking following
the 802.11b standard. While 802.11g also operates entirely within the 2.4 GHz frequency band,
it introduced new modulation schemes that allowed the maximum data transfer rate to be
increased to 54 Mbps (or roughly 5 times that of 802.11b). Due to its higher data rate, 802.11g is
adequate to support the ability of the DCX to make programming content available to portable
wireless devices in the home
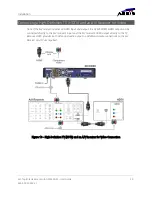
The IEEE 802.11n wireless standard defined the next generation of wireless networking following
the 802.11g standard. 802.11n can operate in either the 2.4 GHz frequency band or the 5 GHz
frequency band, although the standard only requires support for operation within the 2.4 GHz
frequency band (support for 5 GHz operation is optional). The 802.11n also introduced a
number of other improvements (the majority of which are optional) which can help increase the
data transfer rate to as high as 600 Mbps. However, to achieve the maximum data transfer rate,
the wireless devices must include support for most of the optional features within the 802.11n
standard. In practical home networking applications, data transfer rates of up to 300 Mbps are
achievable with currently available 802.11n wireless routers.
.
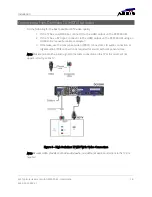
A typical 802.11g wireless network is shown in Figure 6. In this type of home network, the DCX
will automatically configure itself to operate within the 2.4 GHz frequency band and at 802.11g
data transfer speeds once the wireless network information is provided via its WiFi setup
screens. When operating with an 802.11g wireless router, the DCX can support sharing
transcoded programming with other wireless video devices in the home such as smartphones
and tablets. The transcoded programming content provided has a data rate such that it can be
easily streamed across an 802.11g wireless network.
4
In this case, other devices are considered to be devices that are not ARRIS IP set-top boxes with integrated MoCA
functionality.
5
Depending on appropriate network configuration and software support. Please refer to the Transcoding section of
this document for more information.