Evaluation Board User Guide
UG-015
Rev. 0 | Page 9 of 12
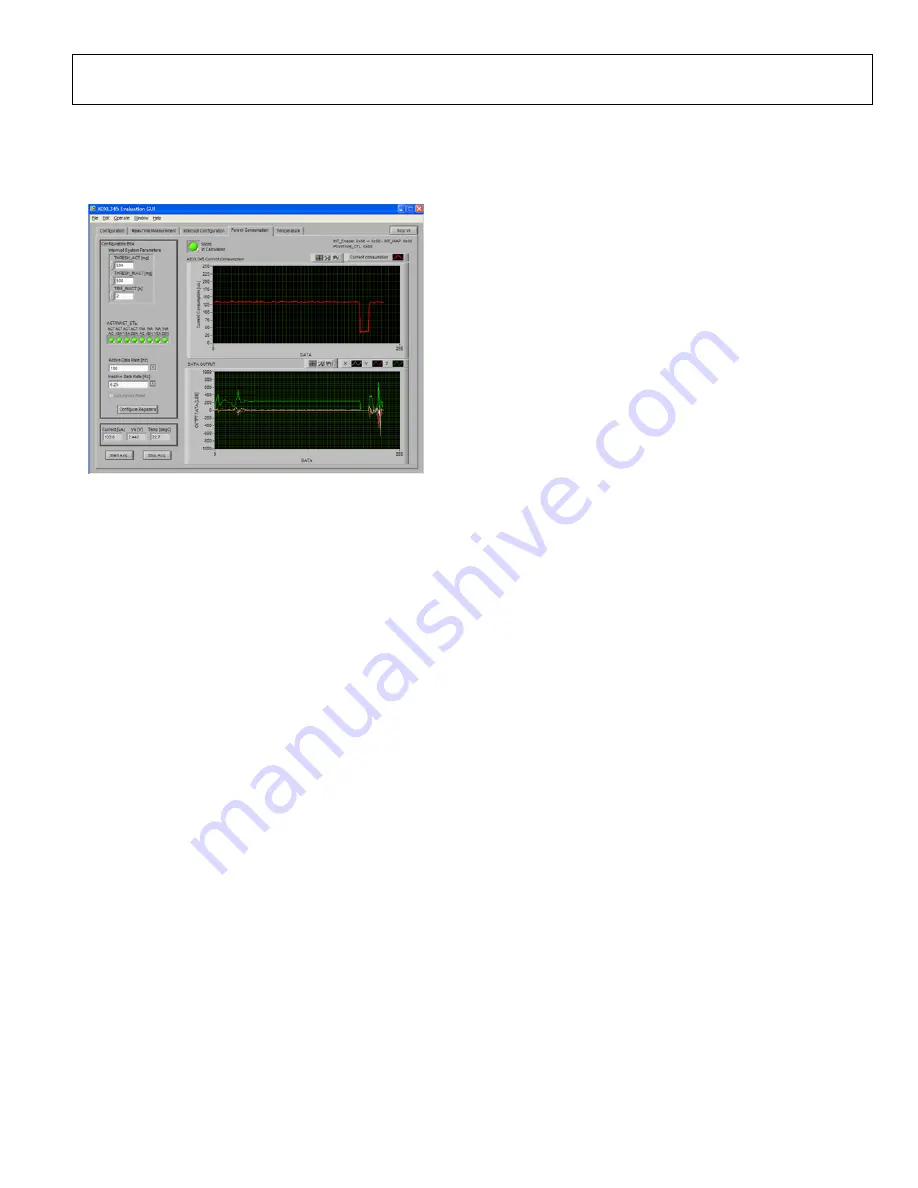
POWER CONSUMPTION TAB
The
Power Consumption
tab shows the advantages of using the
inactivity and activity functions to modulate system power and
obtain overall power savings (see Figure 14).
08
11
9-
01
1
Figure 14. Power Consumption Tab
When inactivity is detected, caused by acceleration below the
amount set in the
THRESH_INACT [m
g
]
box for the amount
of time set in the
TIME_INACT [s]
box, the accelerometer is
placed into a lower data rate as set in the
Inactive Data Rate [Hz]
menu. Because the power of the ADXL345 is modulated with
data rate, an immediate power savings is acheived. When activity is
detected (an acceleration above that set in
THRESH_ACT [m
g
]
box), the part is placed back into a higher data rate as specified
in the
Active Data Rate [Hz]
menu.
Additionally, the
Micro In Calculation
indicator lights up,
signifying that a controller or microprocessor is actively pulling
data from the part or processing it. In addition to power savings
from the ADXL345, more power can be saved by powering
down the microprocessor during periods of inactivity and using
the ADXL345 activity interrupt to wake the microprocessor up
during periods of activity.
The
ACT/INACT_CTL
indicators can be used to enable
different axes in the activity or inactivity events. After updating
the participating axes, thresholds, timers, or data rates, click the
Configure Registers
button. The registers are not updated until
the button is clicked. Additionally, the button updates the registers
only when data acquisition is active. If the button is clicked when
no acquisition is occurring, the button remains inactive until it
is clicked again or until acquisition is started.
To begin data acquisition, click the
Start Acq.
button in the
bottom left corner of the screen. To end data acquisition, click
the
Stop Acq.
button in the bottom left corner of the screen.












