SO-20
Rev 00.00
Pag. 11 di 16
©| Aerservice Equipments S.r.l. | 2020 all rights reserved
é vietata la riproduzione del presente manuale, anche parziale.
RISKS CONNECTED WITH USE OF THE MACHINE
Par
Description
1
Residual risks of the ozone generator
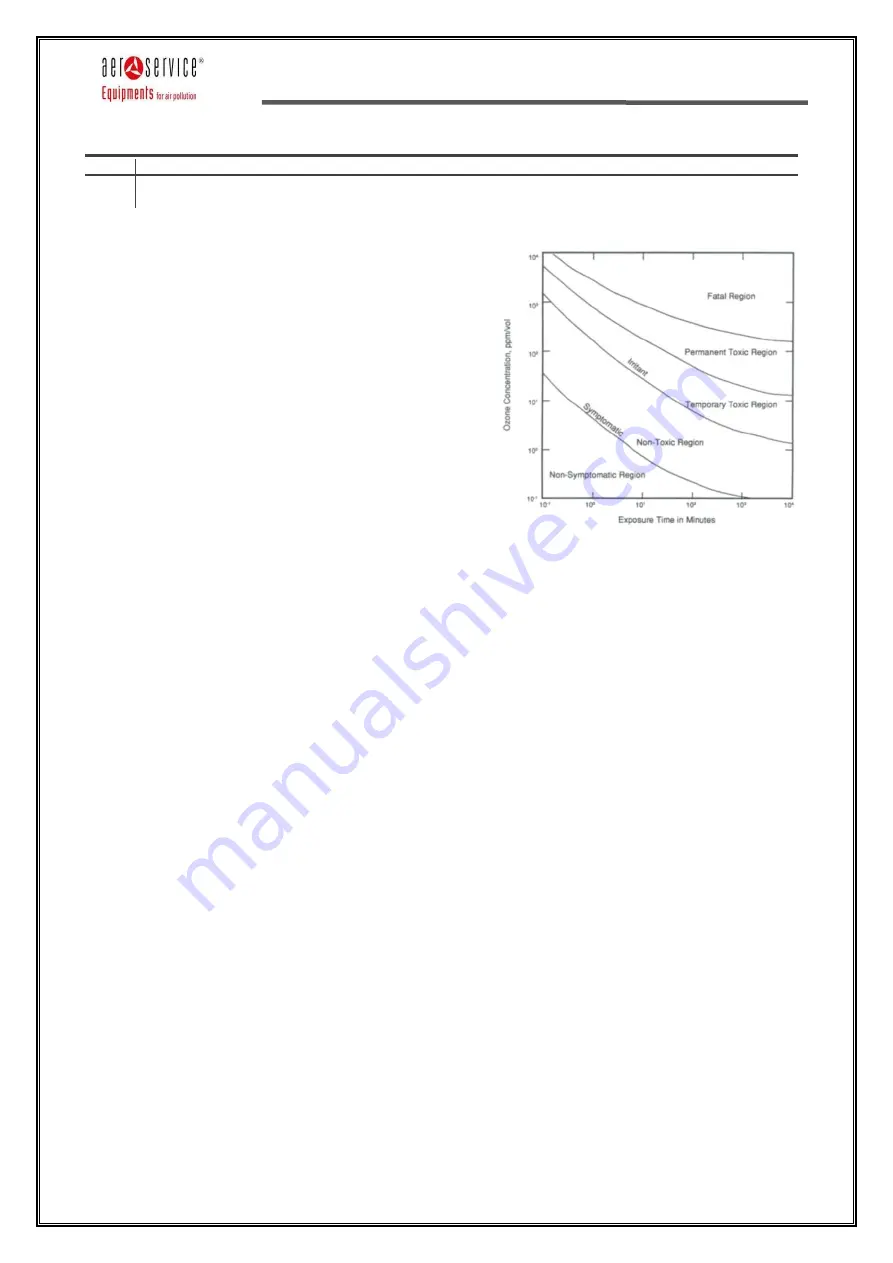
Human tolerance to ozone
Ozone is a toxic gas, after inhalation it can cause diseases if
inhaled in sufficient quantities.
Humans can endure limited ozone exposure, symptoms such
as dry mouth and throat, cough, headache and chest
constriction and close to lethal limits, when the concentration
of ozone increases, serious problems will follow.
Limits * 0.06 ppm for 8 hours a day, 5 days a week (ppm =
parts per million) * 0.3 ppm for up to 15 minutes. These limits
are a maximum acceptable concentration (CMA), these
concentrations are much higher than the olfactory level at
which ozone can be smelled.
The following diagram provides information on times of
exposure to different concentrations and their influences on
humans.
Ozone toxicology
In higher concentrations, ozone can cause health effects after inhalation.
Symptoms such as mucosal irritations and headaches often follow.
These symptoms can also occur during photochemical smog episodes.
Higher concentrations (> 50 ppm) and long-term exposure (> 30 min) can be fatal. However, staying in a
room with this type of concentration is almost impossible.
The long-term effects of ozone exposure are not fully known, but a reduction in lung capacity and an increase
in lung disease should be considered.
To prevent the above health risks, a maximum amount of ozone has been established for the areas where
ozone is used.
This is the so-called maximum permissible concentration, or CMA value. This value describes the maximum
concentration of a substance to which a human can be exposed for a certain period of time.
For a normal five-day, eight-hours-a-day work week, ozone has a CMA value of 0.06 ppm (parts per million
or mg / L). For 15 minutes, the CMA value is 0.3 ppm.
Ozone can be measured in ppm or ppb (parts per billion or μg / L), according to various principles.
With these measurements, you can monitor the ozone concentration in a system.
When the CMA values are reached near the ozone generator, an alarm is issued.
Ozone has a very characteristic odor, which quickly reveals the violation of the CMA value. The level
at which ozone can be smelled is around 0.02 ppm.
Ozone decomposition
When ozone is produced it decays quickly because it is an unstable compound with a relatively short halving
time.
The halving time of ozone in water is much shorter than in air (see table 1). Ozone decays in drinkable water
(pH: 6-8.5), partially in reactive OH radicals.
Hence, the evaluation of an ozone-based process always involves the reaction of two species: ozone and
OH radicals.
When these OH radicals are dominant particles in the solution, it is called the advanced oxidation process
(POA).
Halving of ozone in OH radicals in natural waters is characterized by an initial rapid decrease of ozone,
followed by a second phase in which ozone decreases by first order kinetics.