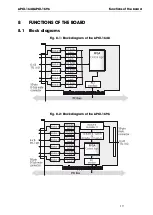
APCI-1648/APCI-1696
Glossary
25
Term
Description
Optical isolation
The technique of using an optoelectric transmitter and receiver
to transfer data without electrical continuity, to eliminate high-
potential differences and transients.
Output current
The maximum amount of current the sensor can supply across
the output signal, expressed as amps DC (A DC).
Output voltage
The nominal voltage output reading when shaft is rotated to
full range, expressed in volts DC /Vo DC)
Parameter
The parameters of a control comprise all for the control
process required numeric values, e.g. for limit values and
technological number.
PCI bus
PCI bus is a fast local bus with a clock rate up to 33 MHz. This
bus is used for processing a great number of data. The PCI bus
is not limited like the ISA and EISA systems.
Protective circuitry
A protective circuitry of the active part is done in order to
protect the control electronic. The simplest protective circuitry
is the parallel switching of a resistance.
Reference voltage
Reference voltages are stable voltages that are used as
reference unit. From them voltages can be derived that are
required for example in current supplies and in other electronic
circuitries.
Resolution
The smallest significant number to which a measurement can
be determined. For example, a converter with 12-bit resolution
can resolve 1 part in 4096.
Sensor
A device that responds to physical stimuli (heat, light, sound,
pressure, motion, etc.) and produces a corresponding electrical
output.
Settling time
The time required, after application of a step input signal, for
the output voltage to settle and remain within a specified error
band around the final value. The settling time of a system
includes that of all of the components of the system.
Short circuit
A short circuit of two clamps of an electric switch is when the
concerning clamp voltage is zero.
Short circuit current
Short circuit current is the current between tow short-circuited
clamps.
Signal delay
The change of a signal affects the following circuitries with
finite velocity; the signal will be delayed. Besides the signal
delay times that are not wanted, the signal delay can be
extended by time switches and delay lines.
TTL
= transistor-transistor logic
A popular logic circuit family that uses multiple-emitter
transistors. The Low signal is defined as a signal of 0.8 V or
lower. A High signal is defined as a signal of 2 V or higher.