41-133S
4
Directional Overcurrent Ground Relays
Types IRP, IRC and IRD
For overcurrent unit:
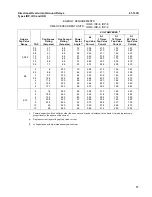
Entering the curve in Figure 24 at multiples of pickup
equal to 4.6, the closing time for instantaneous over-
current is 16 ms. However, the total operating time
for the overcurrent unit is 16 plus 11, which is the
opening time of back contacts of the directional unit,
or 27 ms total operating time for overcurrent unit. The
total time for directional unit is 56 ms, and, since this
is the longest time, 56 ms is the total operating time
of the instantaneous overcurrent circuit.
Entering the curve in Figure 21(page 36) at 4.6, the
1/2 time dial setting gives 140 ms. The total time for
the time-overcurrent circuit is 56 ms directional unit
time plus 16 ms time Aux plus 140 ms = 212 ms.
Example 2:
Let:
Ipol
= 20 amps
Iop
= 23.1 amps
T (tap)
= 1 amp
φ
- 40
°
=
0
°
Entering Figure 23, (page 38) the directional unit
closing time is 12 ms, and the opening time of its
back contacts is 1 ms. The total operating time for
the directional unit is 12 ms.
For overcurrent unit:
Referring to Figure 24, (page 38) the overcurrent unit
contact closing time is about 14 ms. Therefore, the
total operating time for this unit is 14 plus 1 = 15 ms.
In this case the total operating time of relay is 15 ms.
Figure 21 (page 36) gives an operating time of about
50 ms. The time-overcurrent circuit is 12 plus16 plus
50 ms = 78 ms.
4.1 TRIP CIRCUIT
The relay contacts will safely close 30 amperes at
250 volts dc and the seal-in contacts of the indicating
contactor switches will safely carry this current long
enough to trip a circuit breaker.
The indicating contactor switch has two taps that pro-
vide a pickup setting of 0.2 or 2 amperes. To change
taps requires connecting the lead located in front of
the tap block to the desired setting by means of a
screw connection.
4.2 CONTACTS
The moving contact assembly has been factory
adjusted for low contact bounce performance and
should not be changed.
The set screw in each stationary contact has been
factory adjusted for optimum follow and this adjust-
ment should not be disturbed.
4.3 TRIP CIRCUIT CONSTANTS
Indicating Contactor Switch
0.2 ampere tap - 6.5 ohms dc resistance
2.0 ampere tap - 0.15 ohms dc resistance
4.4 AUXILIARY SWITCH (CS-1 OR TR-1)
The CS-1 switch has a dc resistance of 1165 ohms.
The TR-1 telephone relay has a dc resistance of
1500 ohms.
4.5 TYPE IRP RELAY
The IRP relay is designed for potential polarization
and has its maximum torque when the current lags
the voltage by approximately 60 degrees. The shift-
ing of the maximum torque angle is accomplished by
the use of an internally mounted phase shifter as
shown in the internal schematic.
The directional unit minimum pick-up is approxi-
mately 1 volt and 2 amperes at its maximum torque
angle for the directional units used with the 0.5 to 2.5
and 2 to 6 ampere range time overcurrent units. For
the directional units used with the 4-12 ampere range
time overcurrent units the minimum pick-up is 1 volt
and 4 amperes.
4.6 TYPE IRC RELAY
The IRC relay is designed for current polarization
and has its maximum torque when the operating cur-
rent leads the polarizing current by approximately
40
°
.
The directional unit minimum pick-up is 0.5 ampere
Multiples of pickup
lop
T
--------
2.31
0.5
----------
4.6
=
=
=
MPP
lop
lpol
φ
40
°
–
(
)
cos
0.25
-----------------------------------------------------
=
MPP
20
( )
23.1
(
)
0.25
--------------------------
1850
=
=
Multiples of pickup
lop
T
--------
23.1
1
----------
23.1
=
=
=