66 Start-up, control with I/O and ID run
Select the motor identification method (parameter
).
The default value 0 (
) using the identification magnetization is
suitable for most applications. It is applied in this basic start-up procedure. Note
however that this requires that parameter
is set to 1 (
or 2 (
).
If your selection is 0 (
), move to the next step.
Value 1 (
) should be selected if:
• the operation point is near zero speed, and/or
• operation at torque range above the motor nominal torque over a wide speed
range and without any measured speed feedback is required.
If you decide to perform the ID run (value 1 [
]), continue by following the
separate instructions given on page
and then
return to step
DIRECTION OF THE MOTOR ROTATION
.
IDENTIFICATION MAGNETIZATION WITH ID RUN SELECTION 0 (
)
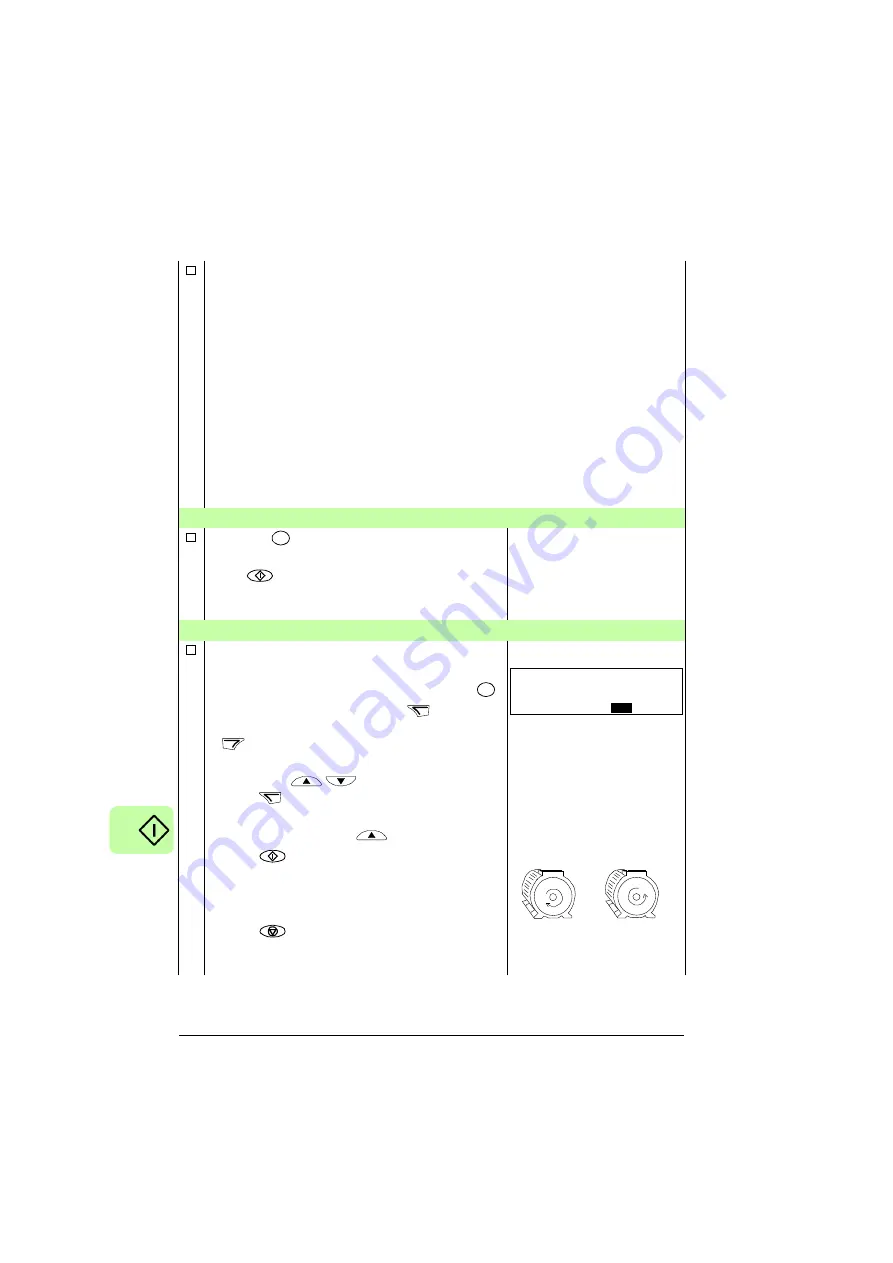
Press key
to switch to local control (LOC
shown on the left).
Press
to start the drive. The motor model is
now calculated by magnetizing the motor for 10
to 15 s at zero speed.
DIRECTION OF THE MOTOR ROTATION
Check the direction of the motor rotation.
• If the drive is in remote control (REM shown on
the left), switch to local control by pressing
.
• To go to the Main menu, press
if the
bottom line shows OUTPUT; otherwise press
repeatedly until you see MENU at the
bottom.
• Press keys
/
until you see “rEF” and
press .
• Increase the frequency reference from zero to
a small value with key
.
• Press
to start the motor.
• Check that the actual direction of the motor is
the same as indicated on the display (FWD
means forward and REV reverse).
• Press
to stop the motor.
To change the direction of the motor rotation:
LOC
REM
LOC
REM
LOC
Hz
SET
FWD
xxx
.
forward
direction
reverse
direction
Summary of Contents for ACS355 series
Page 1: ...ABB machinery drives User s manual ACS355 drives ...
Page 4: ......
Page 16: ...16 ...
Page 32: ...32 Operation principle and hardware description ...
Page 58: ...58 Electrical installation ...
Page 74: ...74 Start up control with I O and ID run ...
Page 106: ...106 Control panels ...
Page 120: ...120 Application macros ...
Page 178: ...178 Program features ...
Page 338: ...338 Fieldbus control with embedded fieldbus ...
Page 368: ...368 Fault tracing ...
Page 404: ...404 Dimension drawings ...
Page 410: ...410 Appendix Resistor braking ...
Page 434: ...434 Appendix Permanent magnet synchronous motors PMSMs ...






























