10
5
Wiring
5.1
Terminal Functions
* Up to +14 V
±
5 % can be supplied by adjusting variable resistor RV1.
RV1 is set to 13.0 V at the factory prior to shipment.
PG Signal Output
The PG signal output (phases A and B) may vary according to installation location on the
motor. Refer to
Fig. 4
for correct wiring.
In general, motor forward direction is counterclockwise (CCW) as viewed from the load
shaft. For YASKAWA’s motor, phase A of PG output leads phase B by a phase angle of 90
°
in clockwise (CW) rotation. According to PG, phase A lags phase B by a phase angle of 90
°
in clockwise (CW) rotation. In this case, when PG is installed at the opposite drive end, con-
nect phases A and B output from PG to the option card as it is.
For YASKAWA’s Inverter motor with PG, PG is installed at the opposite drive end. Then,
phase A lags phase B by a phase angle of 90
°
at motor forward run. (Motor runs CCW as
viewed from PG.) Therefore, when using this motor or similar motors, connect phases A
and B to the option card after replacing phase output. The pulse monitor on this option
shows phase A leading phase B by a phase angle of 90
°
.
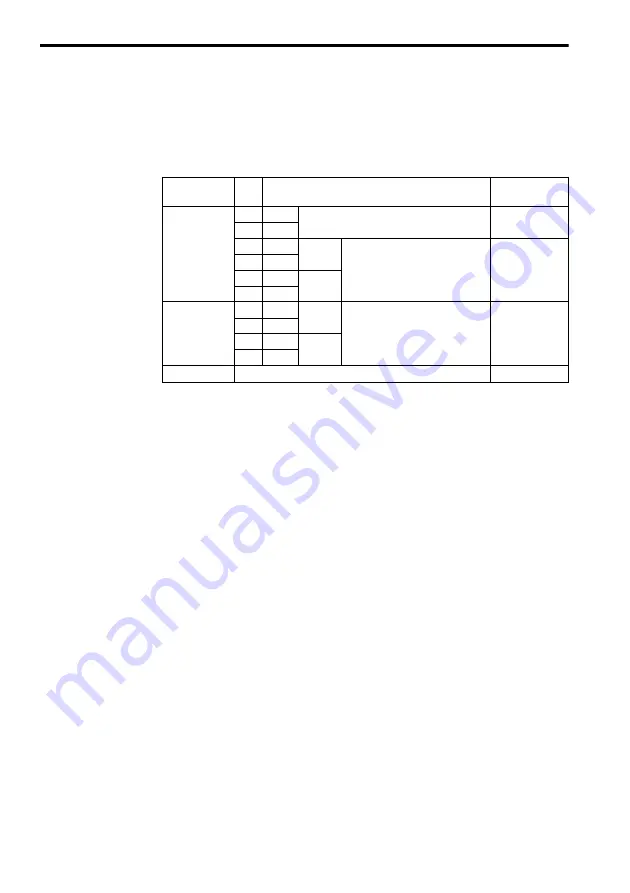
Table 1 Terminal Functions of PG-B2
Terminal Block
Symbol
Pin
No.
Functions
Remarks
TA1
1
+12 V
+12 V power supply
(+12 V
±
5 %, maximum current 200 mA)
*
Power supplies
for PG
2
0 V
3
+
A Pulse
Encoder (Pulse generator, PG)
signal input.
Signal input level
H: +8 V to +12 V
L: +1 V or lower
4
−
5
+
B Pulse
6
−
TA2
1
+
A Pulse
Pulse monitor output.
Open collector
24 V max.
30 mA max.
2
−
3
+
B Pulse
4
−
TA3
Shielded sheath connection terminal



































