MDCS2
U
SER
’
S
M
ANUAL
©
2004
V
IDERE
D
ESIGN
12
6 1394
Interface
Digital image information is transferred from the MDCS2/-C to the host PC
via a 1394 cable. The cable sends video streams from the camera to the PC,
and send commands from the PC to the camera to control exposure,
subsampling, etc. The cable also supplies power to the camera.
6.1 IEEE 1394 Cable
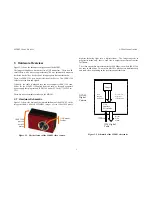
The MDCS2/-C must be connected to the host PC via a 6-pin male-male
IEEE 1394 cable. The maximum length for standard cable is 4.5 m (about
15 feet). The cable supplies both signals and power to the stereo head.
Videre also sells a special 10 m cable for longer distances from the PC.
The distance can also be extended by using a 1394 repeater.
Several 1394-enabled devices can be connected together, as long as the
connection topology doesn’t have any loops. The MDCS2/-C can be
connected at any point in such a topology. At a maximum, it will need
about 60% of the bandwidth of a 400 MBps connection.
6.2 IEEE 1394 Host Interface
The host computer must have an available 1394 ports. Some portables and
desktops come with built-in ports. If these are 6-pin ports, they can be
connected directly to the MDCS2. Sony laptops also support an alternative
4-pin 1394 cabling, which has the signal pins but no power. There are
cables that convert from 4-pin to 6-pin styles; these cables must be used
with an IEEE hub, to supply power to the cameras.
If the host PC doesn’t have a built-in 1394 port, one can be added by
installing a 1394 PCI card or PCMCIA card for laptops. 1394 PCI cards
have 6-pin ports, and supply power. PCMCIA cards do not have the
capability of supplying power, and come with an adapter for supplying
power to the 1394 cable through a wall transformer.
Any 1394 card is suitable, as long as it conforms to OHCI (open host
controller interface) specifications. All current cards do, but some older
cards may not.
6.3 Supplying
Power
Power to the MDCS2 is supplied through the IEEE 1394 cables. The IEEE
1394 system must supply this power, about 1 Watt per camera.
There are two typical PC systems: desktops and laptops.
•
Desktop PCs have either a built-in IEEE 1394 port, or a PCI card with
IEEE 1394 ports. In both cases, the desktop should supply sufficient
power to run the MDCS2.
•
Laptop PCs have either a built-in IEEE 1394 port, or a plug-in PC Card
(sometimes called a PCMCIA card) with several IEEE 1394 ports. In
both cases, the laptop does
not
supply power to the IEEE 1394 bus,
and a source of external power must be used – see below.
External power to the IEEE 1394 bus must have the following
characteristics:
7 to 16 VDC, > 1 W
The IEEE 1394 spec allows up to 40 VDC on the bus, but in practice many
devices such as PC Cards will fail if a voltage higher than 16 VDC or so is
used. We recommend using a 12 VDC source.
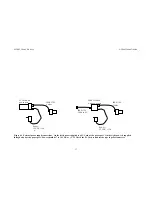
Power can be supplied to the bus through an IEEE 1394 hub or PC Card
with an external port. Most hubs have such a port; most PC Cards do not.
The PC Card supplied by Videre has a power port.
The format of the power plug can vary with the hub or PC Card, so please
check the specifications for the device. Generally, the positive terminal of
the plug is on the inside, and the negative is the outside cylinder.
Figure 6-1 shows the two configurations for supplying power. A wall
transformer converts line voltage to 12 VDC, and is plugged into a hub or
the PC Card.