50
RT-SVX071A-EN
Unit Start-Up
Sequence of Operation
See ACC-APG002*-EN, Application Guide, Symbio™ 700
Controller with Precedent™ Packaged Rooftop Air-
Conditioners.
Ignition Module
Two-stage (IGN) runs self-check (including verification that
the gas valve is de-energized). (IGN) checks the high limit
switches (TC01 and TC02) for normally closed contacts,
the pressure switch (PS) for normally open contacts, and
the flame rollout (FR) switch for continuity.
(IGN) energizes inducer blower on high speed to check
pressure switch closure. If the pressure switch is closed,
the inducer blower starts a 20 second pre-purge (15
seconds on high speed followed by 5 seconds on low
speed). If the pressure switch (PS) is still open, the inducer
blower will continue to be energized on high speed until
pressure switch closure.
After pre-purge completes, the IGN energizes the first
stage gas output for first stage heat demand and energizes
second stage gas output for second stage heat and detects
flame and de-energizes spark.
At this point indoor fan would start with its minimum speed
for the corresponding heat (first stage or second stage)
demand.
The (IGN) enters a normal operating loop where all inputs
are continuously monitored.
If a call for second stage heat is initiated after a call for first
stage heat is established, the (IGN) energizes the second
stage of the gas valve and the second stage of inducer
blower.
When the zone thermostat is satisfied, the (IGN) de-
energizes the gas valve. The (IGN) senses loss of flame.
The (IGN) initiates a 5 second inducer blower post purge.
The Symbio 700 initiates a 90 second indoor blower delay
off at current speed. The (IGN) de-energizes the inducer
blower at the end of the post purge. The Symbio 700 de-
energizes the indoor blower at the end of the selected
indoor blower delay off
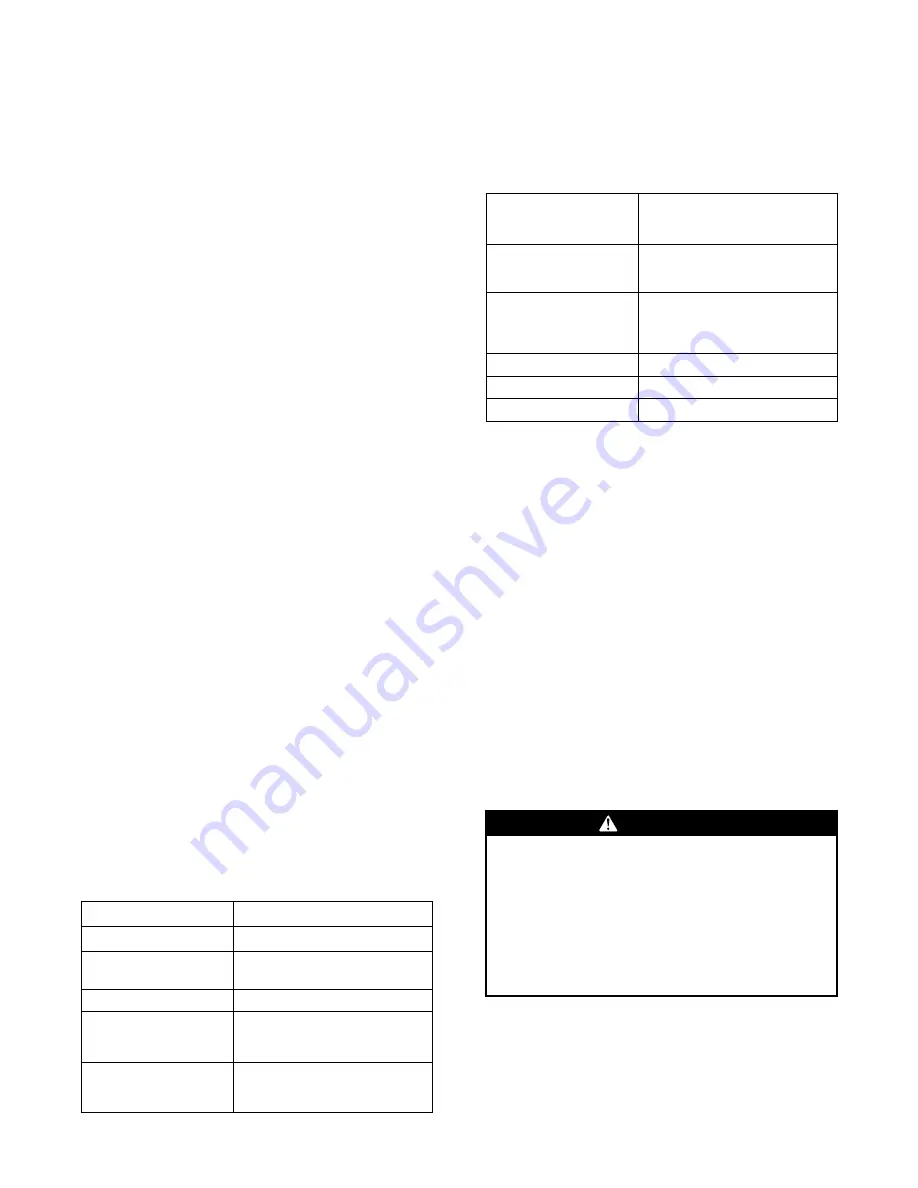
Table 12.
Ignition module diagnostics
Steady OFF
No Power/Failure/ Internal Failure
Steady ON
Normal – No Call for heat
Slow Flash Rate
Normal, call for heat (¾ second on, ¼
second off)
1 Flash
Loss of Communication
2 Flashes
System Lockout: Failed to detect or
sustain flame. (failure to ignite, no
spark, low/no gas pressure, etc.)
3 Flashes
Pressure switch problem detected. (no
vent air flow, bad CBM, closed at initial
call for heat). Auto reset.
Table 12.
Ignition module diagnostics (continued)
4 Flashes
High Limit switch protection device
open (excessive heat in combustion
chamber, low airflow). Auto reset.
5 Flashes
Flame sensed and gas valve not
energized, or flame sensed and no call
for heat.
6 Flashes
Flame Rollout Switch open. (CBM
failure, incorrect gas pressure, incorrect
primary air). Requires manual reset of
the switch.
7 Flashes
Weak Flame
8 Flashes
Internal Error
9 Flashes
Hardware Mismatch
Return Air Smoke Detector
The return air smoke detector is designed to shut off the
unit if smoke is sensed in the return air stream. Sampling
the airflow entering the unit at the return air opening
performs this function.
In order for the smoke detector to properly sense smoke in
the return air stream, the air velocity entering the unit must
be between 500 and 4000 feet per minute. Equipment
covered in this manual will develop an airflow velocity that
falls within these limits over the entire airflow range
specified in the evaporator fan performance tables.
There are certain models however, if operated at low
airflow, will not develop an airflow velocity that falls within
the required 500 to 4000 feet per minute range. For these
models, the design airflow shall be greater than or equal to
the minimum CFM specified in the table provided below.
Failure to follow these instructions will prevent the smoke
detector from performing its design function.
Compressor Start-Up
WARNING
Live Electrical Components!
Failure to follow all electrical safety precautions when
exposed to live electrical components could result in
death or serious injury.
When it is necessary to work with live electrical
components, have a qualified licensed electrician or
other individual who has been properly trained in
handling live electrical components perform these
tasks.
1. Attach a set of service gauges onto the suction and
discharge gauge ports for each circuit.
Proceed to the next Service Test step if continuing from
previous component start-up or until the desired start-
up component test is started.















































