Calibration & Measurement Module for OTKB/OTKBFM
Chapter 5: Operation
TTN030035-D02
Page
12
5.2. Stiffness
Calibration
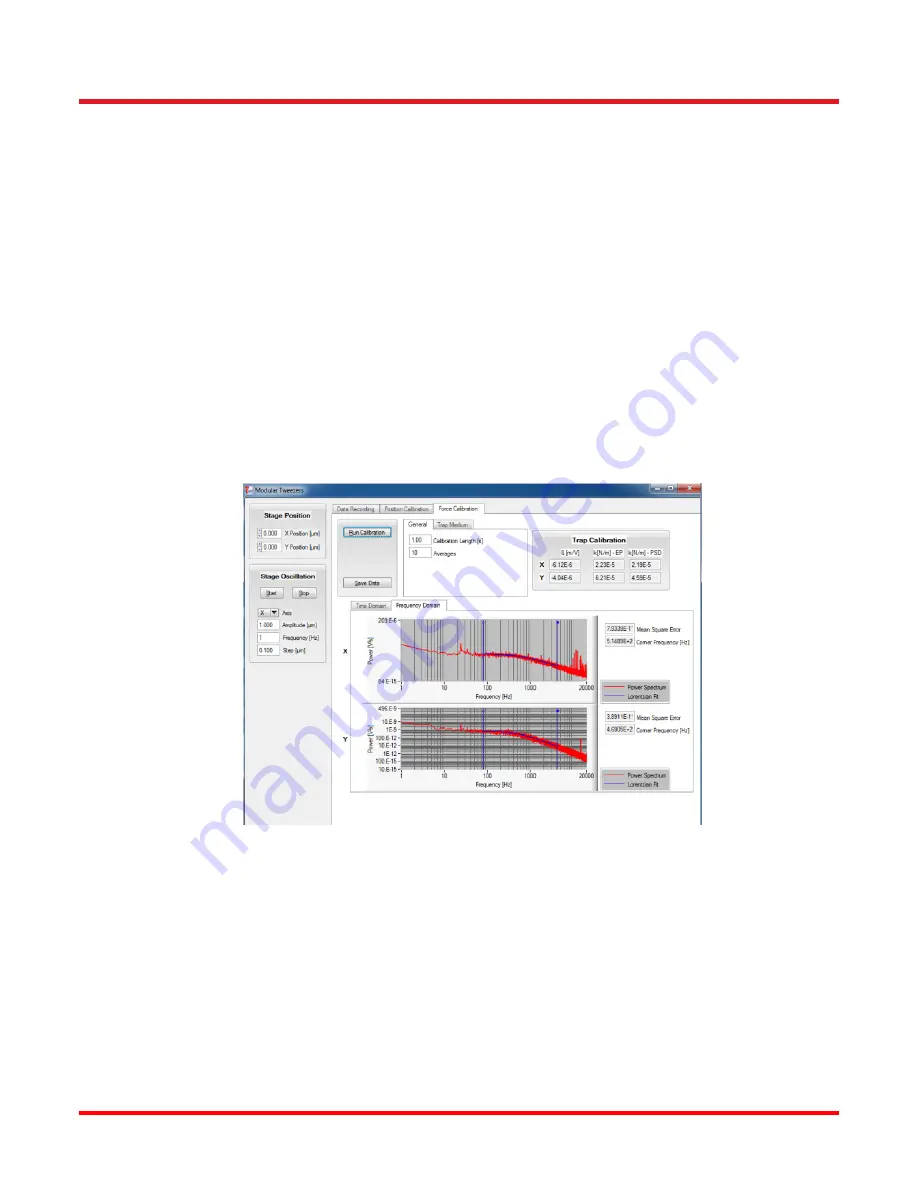
The OTKBFM-CAL software provides two stiffness calibration methods, the so-called PSD Roll-Off and
Equipartition calibration. The first approach uses the fact that the thermal motion of a spherical bead of known
size suspended in water is well characterized. As the laser power is increased, the Brownian motion of the bead
is constrained more and more by the increasing trap force restoring the bead to the center of the trap. A
frequency analysis of the particle position can therefore be used to extract the stiffness parameter. The second
approach is based on the equipartition theorem, which relates the energy of the particle to the temperature at
which the experiment is conducted. Both methods are applied to the data collected from the detector during a
force calibration allowing the user to verify the result.
1. Find a free bead and trap it.
2. Use the data recording tool to verify that the X and Y voltages of the quadrant detector are close to zero. If
this is not the case then adjust the detector to minimize the voltages.
3. Select the “Force Calibration” tab and run the calibration. Depending on the calibration length and the number
of averages which are set, this measurement can take several seconds. The Fourier Transform of the data is
displayed and you can click on the graph to set the lower/upper limit for the fit routine. Each time you change
a limit, the fit is automatically recalculated and the stiffness determined.
4. It is possible to adjust the scale of the plots by holding down the CTRL key and clicking the left mouse button
on the graph to draw a rectangle which defines the new range. In order to zoom out again, hold the CTRL key
and press the right mouse button on the graph surface.
Figure 9
Example PSD Curve Acquired During Force Calibration






















