J1
J4
J2
J5
J3
J6
JP2
PWM
MODE
PSM
JP1
ON
EN
OFF
GND
VIN
VOUT
GND
S-
+
S+
S+
-
S-
TPS82693EVM-207
DC
Power Supply
Load
Oscilloscope
J7
-
+
Chapter 3
SLVU802 – October 2012
Test Configuration
3.1
Hardware Setup
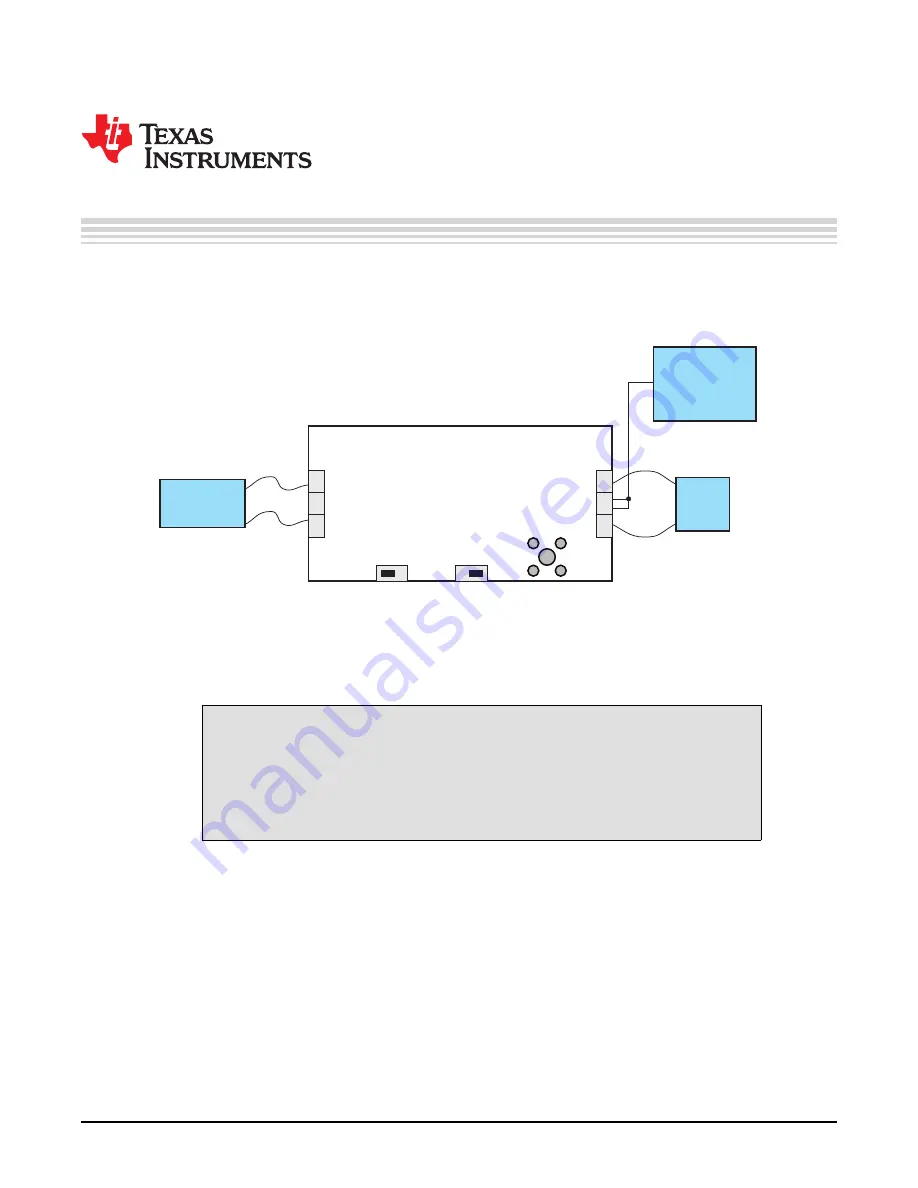
illustrates a typical hardware test configuration.
Figure 3-1. Hardware Board Connection
3.2
Procedure
Follow these procedures when configuring the EVM for testing.
CAUTION
Many of the components on the TPS8269xEVM-207 are susceptible to damage
by electrostatic discharge (ESD). Customers are advised to observe proper
ESD handling precautions when unpacking and handling the EVM, including
the use of a grounded wrist strap, bootstraps, or mats at an approved ESD
workstation. An electrostatic smock and safety glasses should also be worn.
•
Work at an ESD workstation. Make sure that any wrist straps, bootstraps, or mats are connected and
reference the user to earth ground before power is applied to the EVM. Electrostatic smocks and
safety glasses should also be worn.
•
Connect a DC power supply between J1 and J3 on the TPS8269xEVM. Note that the input voltage
should range from 2.3 V to 4.8 V. Keep the wires from the input power supply to EVM as short as
possible and twisted.
•
Connect a DC voltmeter or oscilloscope to the output sense connection of the EVM.
•
A load can be connected between J4 and J6 on the TPS8269xEVM.
•
To enable the converter, connect the shorting bar on JP1 between ENABLE and ON on the
TPS8269xEVM.
•
The TPS8269xEVM has a feature that allows users to switch between PSM under light loads and
forced PWM mode, with jumper JP2.
7
SLVU802 – October 2012
Test Configuration
Copyright © 2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated






























