Functional Description
1258
SLAU723A – October 2017 – Revised October 2018
Copyright © 2017–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
General-Purpose Timers
In periodic, snap-shot mode (TnMR field is 0x2 and the TnSNAPS bit is set in the GPTMTnMR register),
the value of the timer at the time-out event is loaded into the GPTMTnR register and the value of the
prescaler is loaded into the GPTMTnPS register. The free-running counter value is shown in the
GPTMTnV register. In this manner, software can determine the time elapsed from the interrupt assertion
to the ISR entry by examining the snapshot values and the current value of the free-running timer.
Snapshot mode is not available when the timer is configured in one-shot mode.
In addition to reloading the count value, the GPTM can generate interrupts, CCP outputs and triggers
when it reaches the time-out event. The GPTM sets the TnTORIS bit in the GPTM Raw Interrupt Status
(GPTMRIS) register (see
), and holds it until it is cleared by writing the GPTM Interrupt
Clear (GPTMICR) register (see
). If the time-out interrupt is enabled in the GPTM Interrupt
Mask (GPTMIMR) register (see
), the GPTM also sets the TnTOMIS bit in the GPTM
Masked Interrupt Status (GPTMMIS) register (see
). The time-out interrupt can be disabled
entirely by setting the TnCINTD bit in the GPTM Timer n Mode (GPTMTnMR) register. In this case, the
TnTORIS bit does not even set in the GPTMRIS register.
By setting the TnMIE bit in the GPTMTnMR register, an interrupt condition can also be generated when
the Timer value equals the value loaded into the GPTM Timer n Match (GPTMTnMATCHR) and GPTM
Timer n Prescale Match (GPTMTnPMR) registers. This interrupt has the same status, masking, and
clearing functions as the time-out interrupt, but uses the match interrupt bits instead (for example, the raw
interrupt status is monitored via TnMRIS bit in the GPTM Raw Interrupt Status (GPTMRIS) register). The
interrupt status bits are not updated by the hardware unless the TnMIE bit in the GPTMTnMR register is
set, which is different than the behavior for the time-out interrupt. The ADC trigger is enabled by setting
the TnOTE bit in GPTMCTL and the event that activates the ADC is configured in the GPTM ADC Event
(GPTMADCEV) register. The µDMA trigger is enabled by configuring and enabling the appropriate µDMA
channel as well as the type of trigger enable in the GPTM DMA Event (GPTMDMAEV) register. See
The TCACT field of the GPTM Timer n Mode (GPTMTnMR) register can be configured to clear, set or
toggle an output on a time-out event.
If software updates the GPTMTnILR or the GPTMTnPR register while the counter is counting down, the
counter loads the new value on the next clock cycle and continues counting from the new value if the
TnILD bit in the GPTMTnMR register is clear. If the TnILD bit is set, the counter loads the new value after
the next time-out. If software updates the GPTMTnILR or the GPTMTnPR register while the counter is
counting up, the time-out event is changed on the next cycle to the new value. If software updates the
GPTM Timer n Value (GPTMTnV) register while the counter is counting up or down, the counter loads the
new value on the next clock cycle and continues counting from the new value. If software updates the
GPTMTnMATCHR or the GPTMTnPMR registers, the new values are reflected on the next clock cycle if
the TnMRSU bit in the GPTMTnMR register is clear. If the TnMRSU bit is set, the new value will not take
effect until the next time-out.
If the TnSTALL bit in the GPTMCTL register is set and the RTCEN bit is not set in the GPTMCTL register,
the timer freezes counting while the processor is halted by the debugger. The timer resumes counting
when the processor resumes execution. If the RTCEN bit is set, it prevents the TnSTALL bit from freezing
the count when the processor is halted by the debugger.
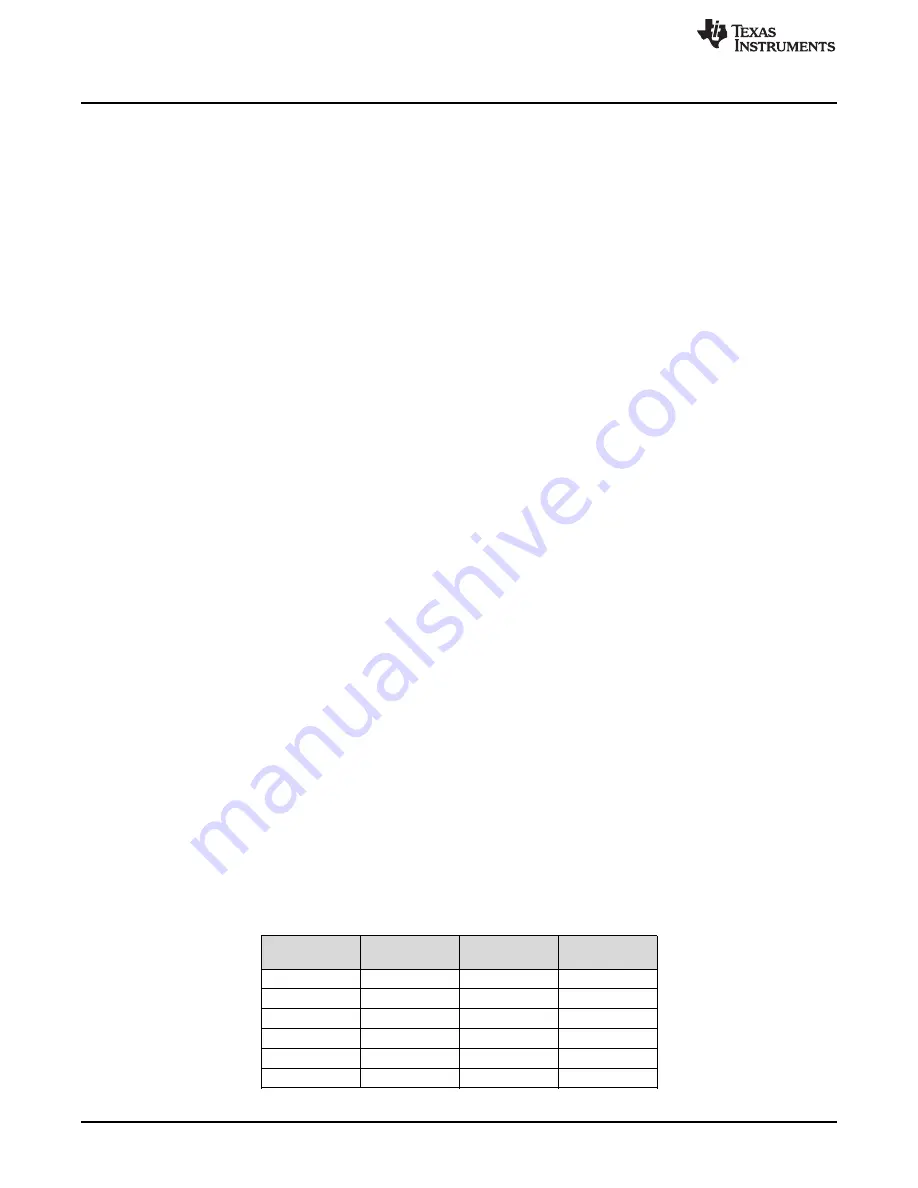
lists a variety of configurations for a 16-bit, free-running timer while using the prescaler. All
values assume a 120-MHz clock with Tc = 8.33 ns (clock period). The prescaler can only be used when a
16- or 32-bit timer is configured in 16-bit mode.
(1)
Tc is the clock period.
Table 18-4. 16-Bit Timer With Prescaler Configurations
Prescale (8-Bit
Value)
No. of Tc
(1)
Maximum Time
Unit
00000000
1
0.548258
ms
00000001
2
1.096517
ms
00000010
3
1.644775
ms
11111101
254
139.2576
ms
11111110
255
139.8059
ms
11111111
256
140.3541
ms






























