Modbus RS485 Stepper Drive User Manual
26
Examples
Mapping target
address
Write to
Parameter original address
0x0F10
←
0x0001 (Pr0.00: Microstep)
0x0F11
←
0x0009 (Pr0.04: inductance value)
0x0F12
←
0x00A1 (Pr2.00: instruction filter time)
0x0F13
←
0x0191 (Pr5.00: peak current)
0x0F14
←
0x0167 (Pr4.19: delay of releasing brake)
0x0F15
←
0x0173 (Pr4.25: software de-jitter delay of position when in position)
0x0F16
←
0x0233 (Pr7.01: encoder resolution)
0x0F17
←
0x0243 (Pr7.09: over-voltage threshold)
0x0F18
←
0x602E (Pr8.46: digital inputs)
0x0F19
←
0x6203 (Pr9.03: PR0 velocity)
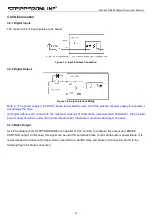
At this point, the mapping of the 10 parameter addresses to the mapped area is complete, and the mapped
addresses can be used for reading and writing instead of the original parameter addresses. For example, if 0x0001
is written to 0x0F10, the operation of reading and writing to 0x0001 can be replaced by "read and write to 0x0F10".
The mapped address is equivalent to a "stand-in" or "proxy" for the original address.
Mapping target address
Reading and writing
Host
0x0F10 (Pr0.00: Microstep)
←--→
Host
0x0F11 (Pr0.04: inductance value)
←--→
0x0F12 (Pr2.00: instruction filter time)
←--→
0x0F13 (Pr5.00: peak current)
←--→
0x0F14 (Pr4.19: delay of releasing brake )
←--→
0x0F15 (Pr4.25: software de-jitter delay of position when in
position)
←--→
0x0F16 (Pr7.01: encoder resolution)
←--→
0x0F17 (Pr7.09: over-voltage threshold)
←--→
0x0F18 (Pr8.46: digital inputs)
←--→
0x0F19 (Pr9.03: PR0 velocity)
←--→
Message Example
Conditions: Drive ID is 1, motor is stationary.
(1) Mapping
Master→Slave:
01 10 0F 10 00 0A 00 00 01 00 09 00 A1 01 91 01 67 01 73 02 33 02 43 60 2E 62 03 4B 43
Slave → Master:
01 10 0F 10 00 0A 42 DF