– 4 –
SECTION 1
SERVICING NOTES
MODEL IDENTIFICATION
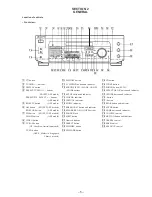
– Rear view –
1234
PART No.
MODEL
PART No.
DE 335: US model
4-218-844-0
[]
DE 335: Canadian model
4-218-844-1
[]
DE 335: Australian model
4-218-844-2
[]
DE 335: Malaysia, Singapore models
4-218-844-3
[]
V 323
4-218-844-4
[]
DE 335: E model
4-218-844-5
[]
DE 335: AEP model
4-218-844-6
[]
SE 391
4-218-844-7
[]
SAFETY CHECK-OUT
After correcting the original service problem, perform the follow-
ing safety check before releasing the set to the customer:
Check the antenna terminals, metal trim, “metallized” knobs,
screws, and all other exposed metal parts for AC leakage.
Check leakage as described below.
LEAKAGE TEST
The AC leakage from any exposed metal part to earth ground and
from all exposed metal parts to any exposed metal part having a
return to chassis, must not exceed 0.5 mA (500 microamperes).
Leakage current can be measured by any one of three methods.
1. A commercial leakage tester, such as the Simpson 229 or RCA
WT-540A. Follow the manufacturers’ instructions to use these
instruments.
2. A battery-operated AC milliammeter. The Data Precision 245
digital multimeter is suitable for this job.
3. Measuring the voltage drop across a resistor by means of a
VOM or battery-operated AC voltmeter. The “limit” indica-
tion is 0.75 V, so analog meters must have an accurate low-
voltage scale. The Simpson 250 and Sanwa SH-63Trd are ex-
amples of a passive VOM that is suitable. Nearly all battery
operated digital multimeters that have a 2 V AC range are suit-
able. (See Fig. A)
Fig. A.
Using an AC voltmeter to check AC leakage.
1.5 k
Ω
0.15
µ
F
AC
voltmeter
(0.75 V)
To Exposed Metal
Parts on Set
Earth Ground