6.5
Configuring PROFINET IO
6.5.1
General information about communication via PROFINET IO
Communication cycle
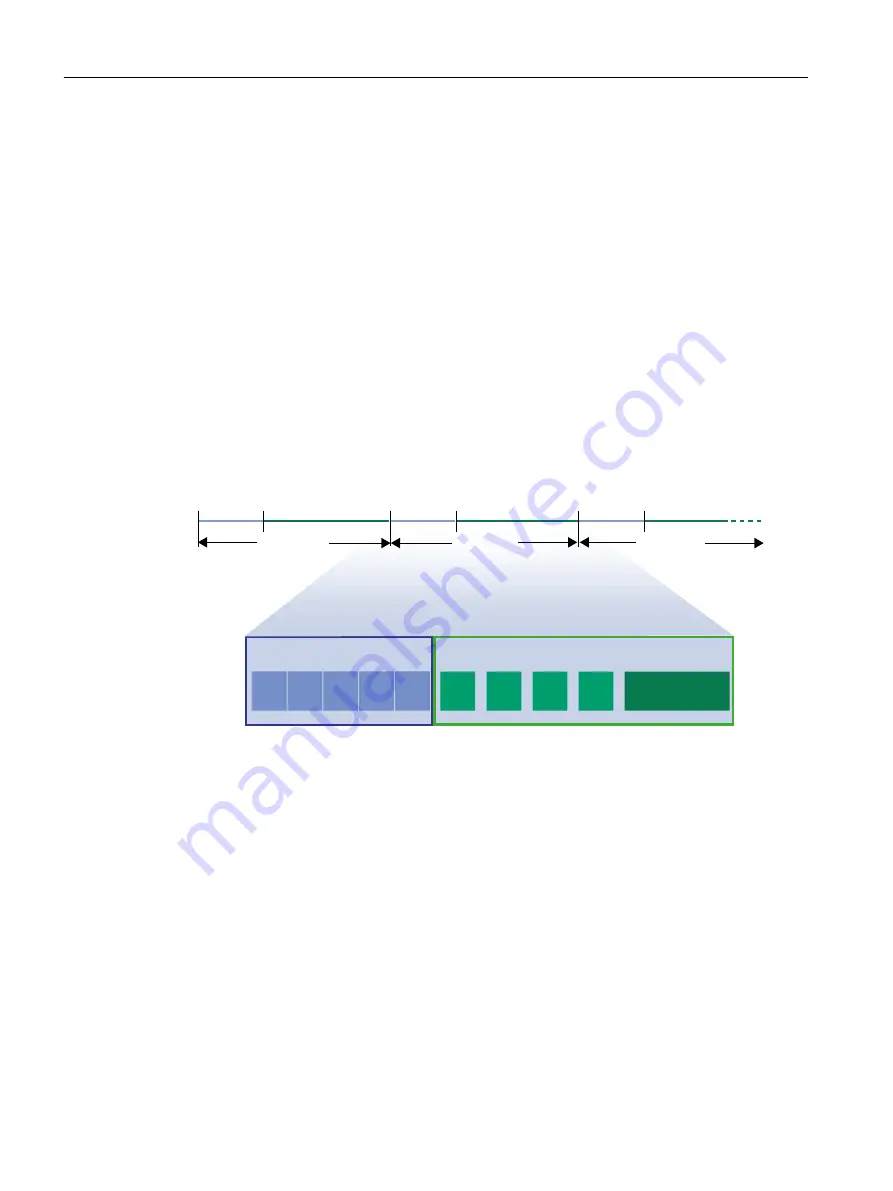
In PROFINET, the communication cycle is subdivided into different, time-specific intervals.
The first interval is used for isochronous real‑time communication (IRT), followed by real‑time
communication (RT) and standard TCP/IP communication. The bandwidth reservation for IRT
ensures that RT communication and standard communication have no effect on the
transmission of IRT telegrams, which are important for motion control applications.
The following figure shows how the PROFINET communication cycle is divided into
isochronous real-time communication (IRT), real-time communication (RT), and standard TCP/
IP communication.
,57LQWHUYDO
,57
LQWHUYDO
,57LQWHUYDO
,VRFKURQRXVFRPPXQLFDWLRQ
57FRPPXQLFDWLRQ
6WDQGDUGFRPPXQLFD
WLRQ
&\FOH
&\FOH
WLPHZLQGRZ
&\FOHQ
,57GDWD
57'DWD
7&3,3GDWD
7&3,3
7&3,3
7&3,3
Figure 6-7
PROFINET communication cycle
Isochronous real-time Ethernet
STEP 7 can be used to configure PROFINET devices supporting data exchange via
isochronous real-time Ethernet (IRT). IRT telegrams are transferred deterministically via
planned communication paths in a defined sequence to achieve the best possible synchronism
and performance.
IRT requires special network components supporting a planned data transfer.
Isochronous operation and mode
Equidistant mode and isochronous mode function similarly in PROFINET IO to the way they
function in PROFIBUS DP.
For PROFIBUS DP, in isochronous operation all nodes are synchronized using a Global
Control Signal created by the DP master.
Parameter assignment / addressing
6.5 Configuring PROFINET IO
SIMOTION D4x5-2
144
Commissioning and Hardware Installation Manual, 03/2018, A5E33441636B
















































