Supplementary information
15.10 Communication via fault-tolerant S7 connections
CPU 410-5H Process Automation
272
System Manual, 09/2014, A5E31622160-AB
15.10.1
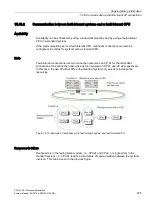
Communication between fault-tolerant systems
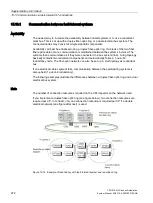
Availability
The easiest way to increase the availability between linked systems is to use a redundant
plant bus. This is set up with a duplex fiber-optic ring or a dual electrical bus system. The
connected nodes may consist of simple standard components.
Availability can best be enhanced using a duplex fiber-optic ring. If a break of the two-fiber
fiber-optic cable occurs, communication is maintained between the systems involved. The
systems then communicate as if they were connected to a bus system (line). A ring topology
basically contains two redundant components and automatically forms a 1-out-of-2
redundancy node. The fiber-optic network can also be set up in star topology as redundant
bus.
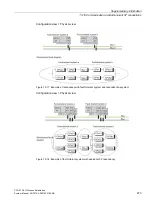
If one electrical cable segment fails, communication between the participating systems is
also upheld (1-out-of-2 redundancy).
The following examples illustrate the differences between a duplex fiber-optic ring and a dual
electrical bus system.
Note
The number of connection resources required on the CPs depends on the network used.
If you implement a duplex fiber-optic ring (see figure below), two connection resources are
required per CP. In contrast, only one connection resource is required per CP if a double
electrical network (see figure after next) is used.
Figure 15-16 Example of redundancy with fault-tolerant system and redundant ring