Copyright © Siemens AG 2016. All rights reserved
326
ERTEC 200P-2 Manual
Technical data subject to change
Version 1.0
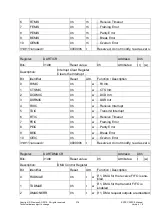
Once configured, the unit automatically reads data from the expander into the register
DATA_IN_n (when CTRL_n (IN) = 1) and writes data from the register DATA_OUT_n into
the expander (when CTRL_n (OUT) = 1), where n = expander 1 to 4.
The register ADDR_n is used to store the associated slave address of the various ex-
panders. Although EX_ADDR_n is implemented as an 8-bit register, only bits 7....1 are
used as slave address. Bit 0 of the register is used by the "IO Expansion Unit" to distin-
guish between a read access and a write access.
In automatic operation, the registers EX_ADDR_n and EX_DATA_OUT_n must be con-
figured before access can be started by writing to EX_CTRL_n. Depending on the setting
of the register CTRL_n (MODE), this function can be used either periodically or as re-
quired.
If this register is configured for "as required" (= 0), then CTRL_n (IN) and CTRL_n (OUT)
will be reset after the I
2
C access. The service has to be disabled during the direct access
to the I
2
C bus (CTRL_n (OUT) = CTRL_n (IN) = 0 ).
The CTRL_n (status) bit indicates the success of the last transfer. If an error has oc-
curred, this bit is set to ‘1’; whereas it remains ’0’ after a successful transfer. The internal
status register for the I
2
C module is monitored here.
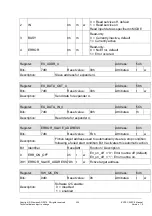
The activated "IO Expansion Unit" takes control of the I
2
C macro. This prevents the
ARM926 from accessing the I
2
C until one of the four expanders has been processed. The
ARM926 must deactivate all IO Expander services in order to access the I
2
C. Then the
ARM926 must wait until the register CTRL_n (BUSY) indicates the end of all automatic
transfers. The microprocessor now has full access to the I
2
C and operates in immediate
access mode. Because the default value set by the software is no longer valid, the regis-
ter I2C_CNTR must be reconfigured to switch from immediate access to automatic opera-
tion.
2.3.10.6.3 Important Software rules
1. Ensure for consecutive sequences of start and stop conditions that a non-existent
slave address is loaded into the data register before issuing the stop condition. Af-
ter issuing the stop condition, the contents of the data register are output as slave
address, followed by the stop condition. In automatic operation, the contents of the
Error Slave Address register are used as slave address. This routine can be acti-
vated using bit ’0’ in the Error Slave Address register.
2. If a deadlock occurs on the I
2
C bus, write accesses to bit 7 in the register
EX_Control_1 can be used to influence the SCL clock pin. Setting this bit causes
SCL to become “low”. Conversely, resetting the bit switches SCL to “high”.
3. The register I2C_DATA does not have the same source or the same target when it
is addressed with a write/read access. When this register is read, only the data
transferred on the I
2
C bus is accessible. This means that the read value can differ
from the written value for a write with a subsequent read.
4. To perform the handshake with the I
2
C, it is expected that the ARM926 either polls
the IFLG interrupt flag of the CNTR register, or activates the interrupt output. Once
an interrupt has been recognized, a wait time of at least 2 s must be observed.
Only then the next action on the I
2
C bus can be initiated. Otherwise errors can oc-
cur during the next address/data transfer.
5. The I
2
C controller has a bug which occurs in this way:
Содержание ERTEC 200P
Страница 1: ...ERTEC 200P 2 Enhanced Real Time Ethernet Controller Manual ...
Страница 309: ...Copyright Siemens AG 2016 All rights reserved 309 ERTEC 200P 2 Manual Technical data subject to change Version 1 0 ...
Страница 492: ...Copyright Siemens AG 2016 All rights reserved 492 ERTEC 200P 2 Manual Technical data subject to change Version 1 0 ...