Copyright © Siemens AG 2016. All rights reserved
15
ERTEC 200P-2 Manual
Technical data subject to change
Version 1.0
1 INTRODUCTION
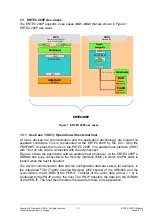
1.1 Overview of the ERTEC 200P
In the following manual ERTEC 200P means ERTEC 200P Step1/Step2 and ERTEC
200P-2 means ERTEC 200P Step2.
The ERTEC 200P provides switch functions covering all necessary mechanisms for
targeted frame forwarding. The ERTEC 200P also features a function for preparing
frame data for a given user interface.
ERTEC 200P adds IRT communication to the current IRT, RT and NRT communication
for Ethernet. Standard NRT mode is not suitable for real-time control technology appli-
cations for modern control and drive concepts, as data has to be processed by the
TCP/IP stack and runtimes in the network are variable. Improvements can be achieved
with RT, which operates using the same switch mechanisms as NRT. RT prioritizes the
frames, increasing network determinism, and processes data for the end nodes to
achieve greater throughput.
A further increase in determinism is achieved by switching to IRT, in which cyclic com-
munication runs in reserved time phases. A distinction is drawn between address-
based forwarding and topological forwarding (planned communication).
Even better performance can be achieved with IRT High Performance, which operates
on the basis of fast-forwarding multicast addresses (with frame ID in Octet 5/6) and
uses pack frames (which pack together multiple devices). This significantly reduces the
cut through time, which in turn leads to much shorter cycle times.
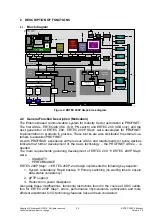
1.1.1 Mechanisms for PROFINET IO (NRT communication)
The basis for NRT requirements is switch functions for standard Ethernet (NRT) with
NRT fragmentation for shorter send clocks. This is what is known as the address-
based forwarding of frames. The required function is specified in the IEEE 802.1D /1/
and IEEE 802.1Q /2/ standards (see chapter 7.2
X
). In addition to the switch functions,
there is another function for receiving or for transferring data frames over the user
interface to the host. The requirements for standard Ethernet also include all those
functions that are needed with external PHYs or, as in the case of ERTEC 200P, with
the integrated PHYs.
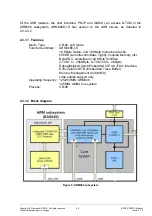
1.1.2 Mechanisms for PROFINET IO (RT communication) RTC1/2
The requirements for soft real-time Ethernet (RT) are based on Functional Specifica-
tion PROFINET-IP. Below are just the main RT requirements:
-
Supports cyclic and acyclic RT traffic
-
Greater frame traffic determinism with priority tag option for RT data
-
Option of high-priority forwarding for RT frames in the PN-IP
-
Improved user interface performance achieved as a result of the hardware pro-
cessing the user data in process images
-
Option of high-priority forwarding of acyclic RT frames to the user interface
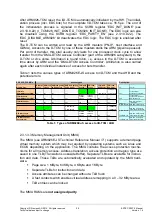
1.1.3 Mechanisms for PROFINET IO (IRT communication)
RTC3
With IRT, cyclic communication operates in reserved time phases. You can choose
between address-based forwarding and topological forwarding (planned communica-
tion). The cut through time is ca. 2.1 µs (incl. PHY).
Содержание ERTEC 200P
Страница 1: ...ERTEC 200P 2 Enhanced Real Time Ethernet Controller Manual ...
Страница 309: ...Copyright Siemens AG 2016 All rights reserved 309 ERTEC 200P 2 Manual Technical data subject to change Version 1 0 ...
Страница 492: ...Copyright Siemens AG 2016 All rights reserved 492 ERTEC 200P 2 Manual Technical data subject to change Version 1 0 ...