EB 8048 EN
31
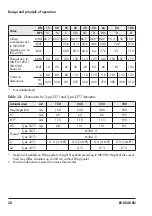
Mounting
Risk of personal injury due to preloaded
springs.
Actuators with preloaded springs are under
tension. They can be identified by the long
bolts protruding from the bottom of the actu
-
ator.
Î
Before starting any work on the actuator,
relieve the compression from the pre
-
loaded springs (see associated actuator
documentation).
Diaphragm damage through the use of an
incompressible medium.
Closing the valve when the shut-off valves
upstream and downstream of the valve are
closed may lead to the diaphragm rupturing
in plants with liquid media flowing through
them.
Î
Only close the valve when the shut-off
valves upstream and downstream of the
valve are open.
To test the valve functioning before start-up
or putting back the valve into operation, per-
form the following tests:
5.4.1
Leak test
The plant operator is responsible for per-
forming the leak test and selecting the test
method. The leak test must comply with the
requirements of the national and internation-
al standards that apply at the site of installa-
tion.
Our after-sales service can support you to
plan and perform a leak test for your plant.
Valve malfunction due to a leaking dia-
phragm.
Î
The screw at the test connection (4.4) can
be replaced by a pressure sensor to
monitor the diaphragm (6.3) for leak
-
age.
1.
Close the valve.
2. Slowly apply the test medium to the inlet
space upstream of the valve. A sudden
surge in pressure and resulting high ve-
locities can damage the valve.
3.
Open the valve.
4.
Apply the required test pressure.
5.
Check the valve for leakage to the atmo
-
sphere.
6.
Depressurize the pipeline section and
valve.
7. Rework any parts that leak (see informa
-
tion below under Adjusting the packing)
and repeat the leak test.
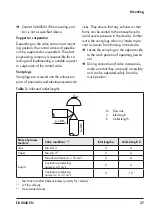
Adjusting the packing
A label on the valve bonnet or yoke indi-
cates whether an adjustable packing is in-
stalled (see section 2).
WARNING
!
NOTICE
!
Tip
NOTICE
!