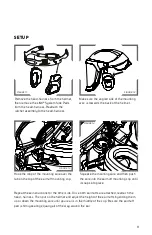
4
™
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Improper selection, fit, use, or maintenance of this product can result
in temporary or permanent hearing loss. This product is intended
for occupational use in accordance with applicable standards or regulations for your location,
industry, and activity (see Employer Responsibilities, page 5). Familiarity with standards and
regulations related to the use of this protective equipment is recommended, even if they
do not directly apply to you. If self-employed or if used in a non-occupational setting, refer
to Employer Responsibilities and Product User Safety Instructions. Go to rpbsafety.com/
importantsafetyinformation/ for helpful links to OSHA and other content.
Employers:
Read this manual and carry out the Employer Responsibilities (page 5).
Product users:
Read this manual and follow the Product User Safety Instructions (page 6).
Check website for updates.
Product manuals are regularly updated.
Visit www.rpbsafety.com/resources/for the most recent version of this manual before using the
product.
WARNING
PROTECTIONS PROVIDED AND LIMITATIONS
HEARING PROTECTION
The Quiet-Link
™
Ear Defender system provides an Noise Reduction Rating (NRR) of 25.
The Quiet-Link
™
Ear Defender helmet mounted system is not designed to be used with any
other respirator or helmet besides the Z-Link
®
and T-Link
®
.
ATTENUATION DATA
Table 1.1
TEST
FREQUENCIES (Hz)
125
250
500
1000
2000
3150
4000
6300
8000
NRR
MEAN
ATTENUATION (dB)
19.7
21.0
27.5
38.4
38.3
45.2
44.5
48.6
47.6
25
STANDARD
DEVIATION (dB)
2.5
2.8
2.8
3.5
2.9
3.9
3.0
3.3
2.7
The level of noise entering a person’s ear, when a hearing protector is worn as directed, is closely
approximated by the difference between the A-weighted environmental noise level and the NRR.
Example:
1.
The environmental noise level as measured at the ear is 92 dBA.
2.
The NRR is 25 decibels (dB)
3.
The level of noise entering the ear is approximately equal to 67dBA.
For noise environments dominated by frequencies below 500Hz, the C-weighted environmental
noise level should be used in determining required NRR. Refer to Table 1.1. for attenuation data by
frequency. Improper fit of this device will reduce its effectiveness in attenuating noise. Although
hearing protectors can be recommended for protection against harmful effects of impulse noise,